Scenario Description
For command records, when managing large asset clusters through JumpServer, we recommend transferring commands to an Elasticsearch cluster to alleviate database pressure. Currently, JumpServer supports periodic index creation when integrating with Elasticsearch, facilitating future management and archiving.
Operation Instructions
Here are the environment requirements and the operations for integrating with Elasticsearch.
Environment Requirements
Integrating with Elasticsearch
You can refer to the official documentation for the installation process of Elasticsearch at <https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/install-elasticsearch.html>
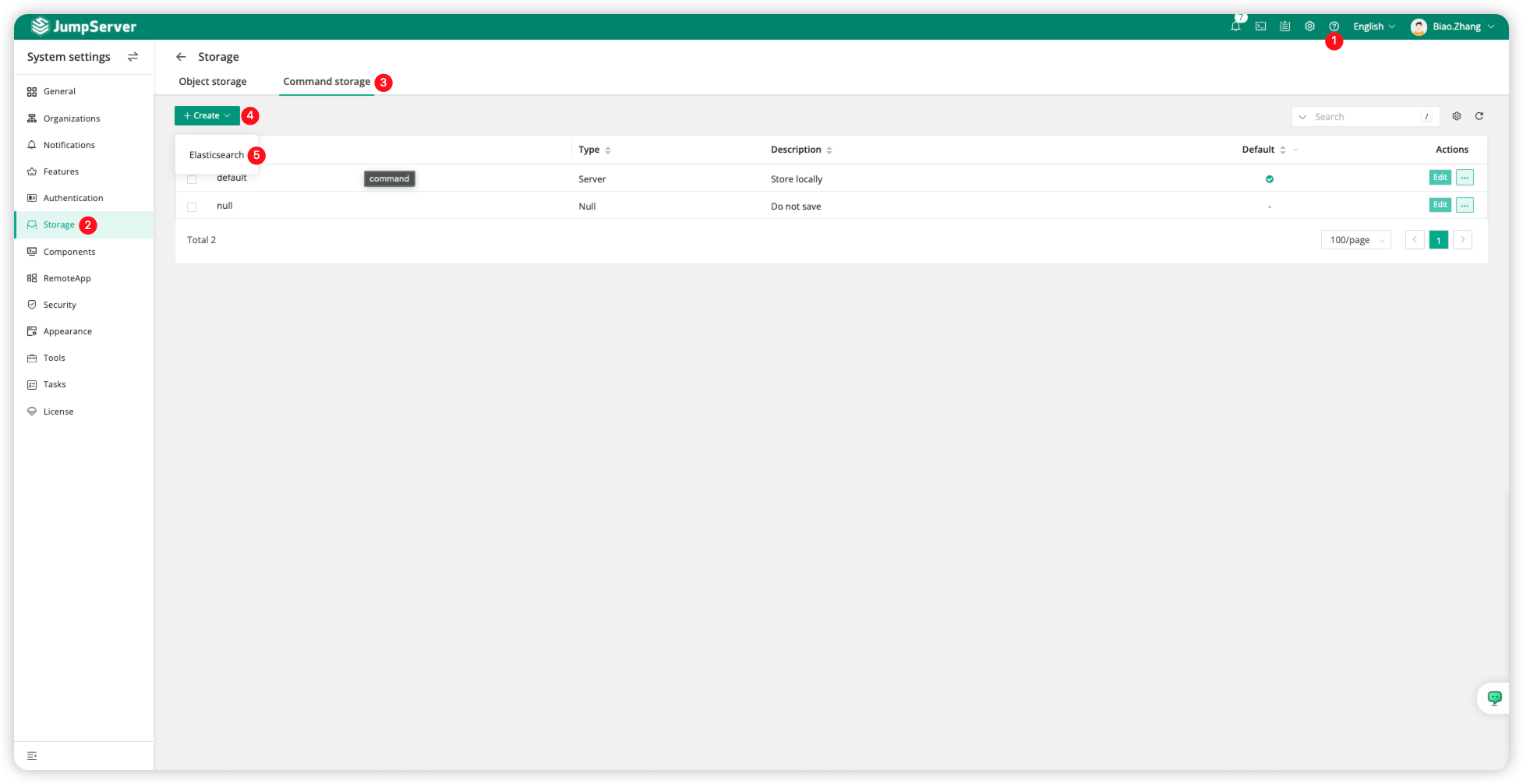
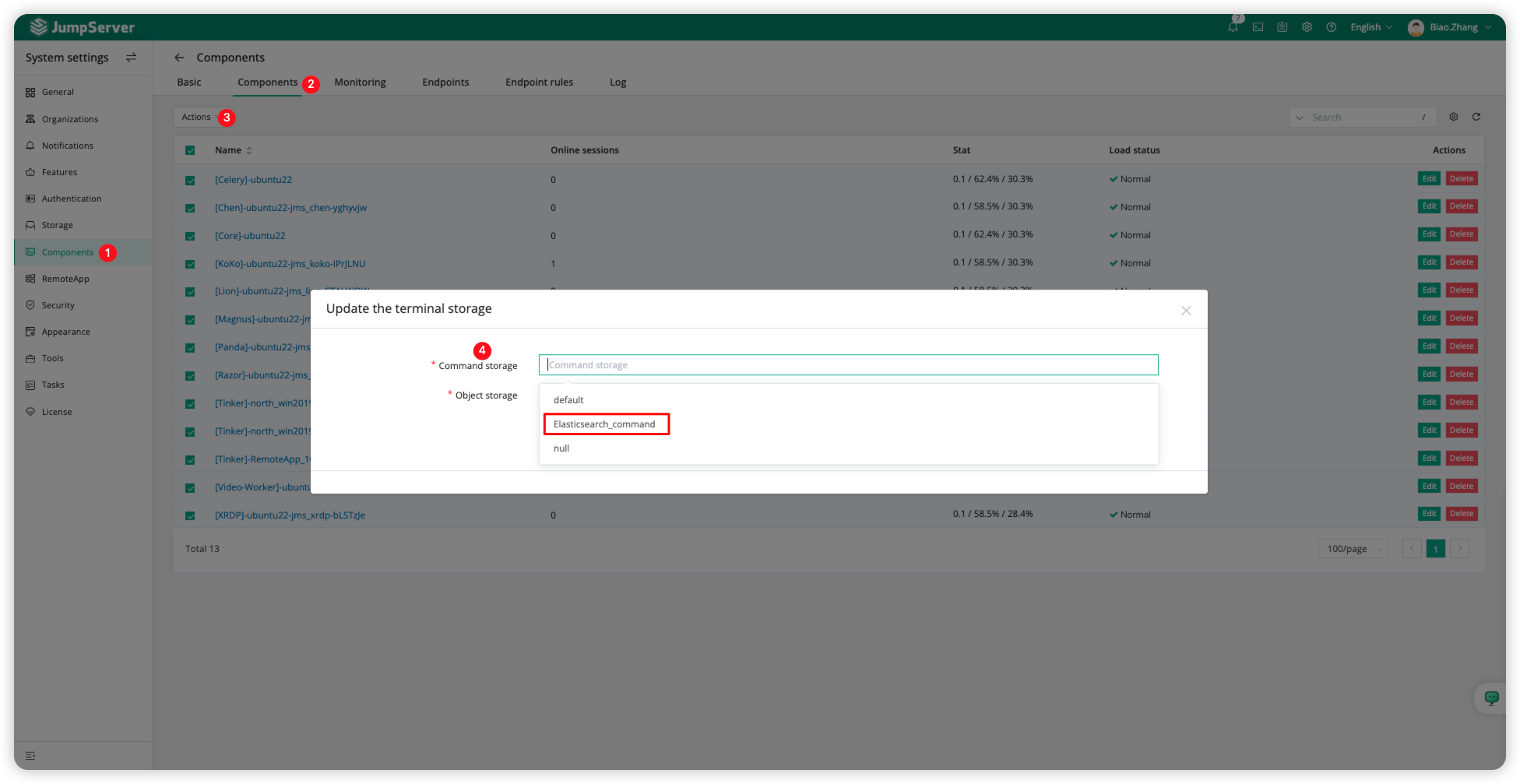
Click the <gear> icon in the upper right corner of the JumpServer page, switch to the <System settings> page, then click <Storage>, and select <Command storage> to <Create> an Elasticsearch resource.
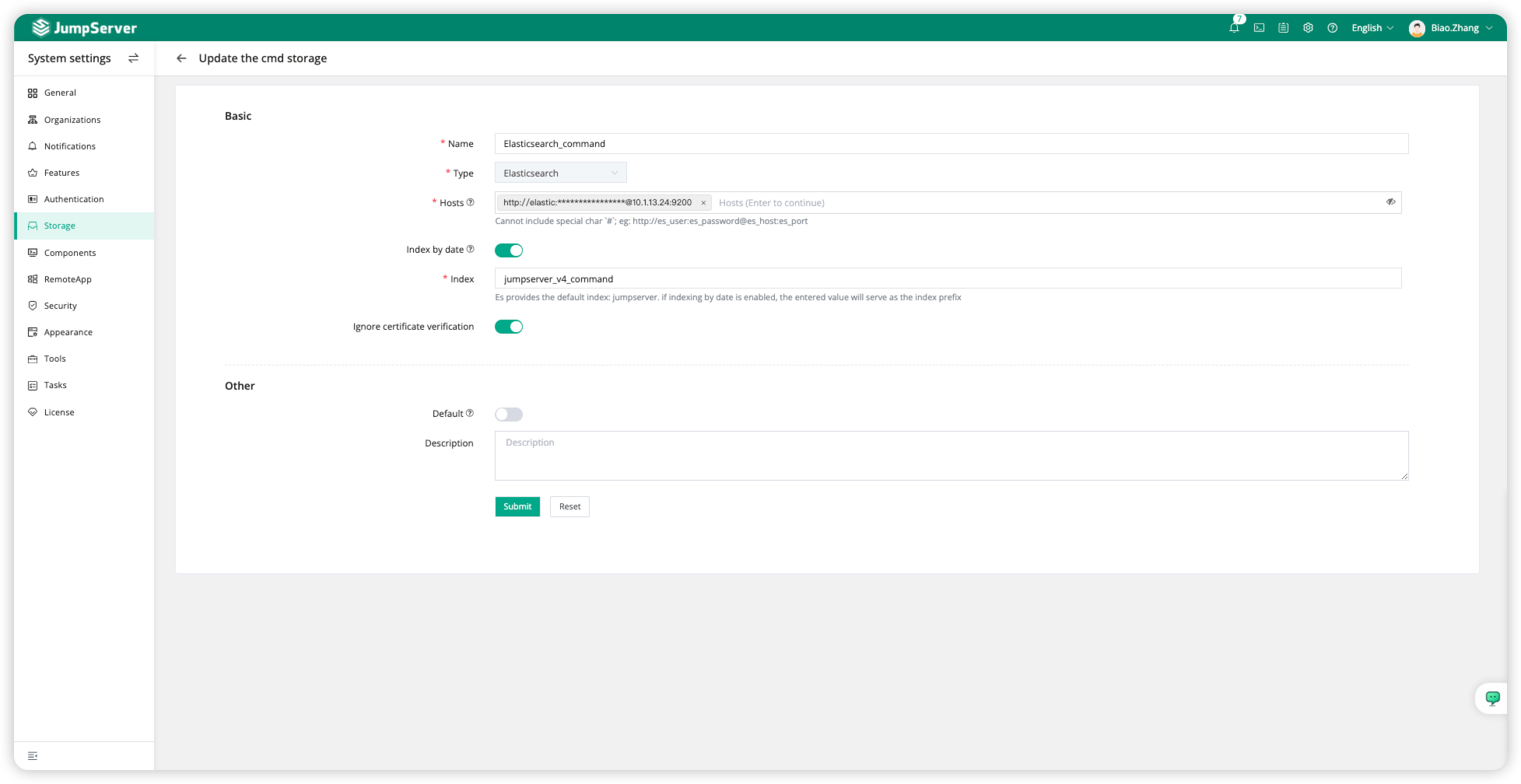
On the Create Command Storage page, configure the following information for Elasticsearch: Hosts, index by date, index, and Ignore certificate verification.
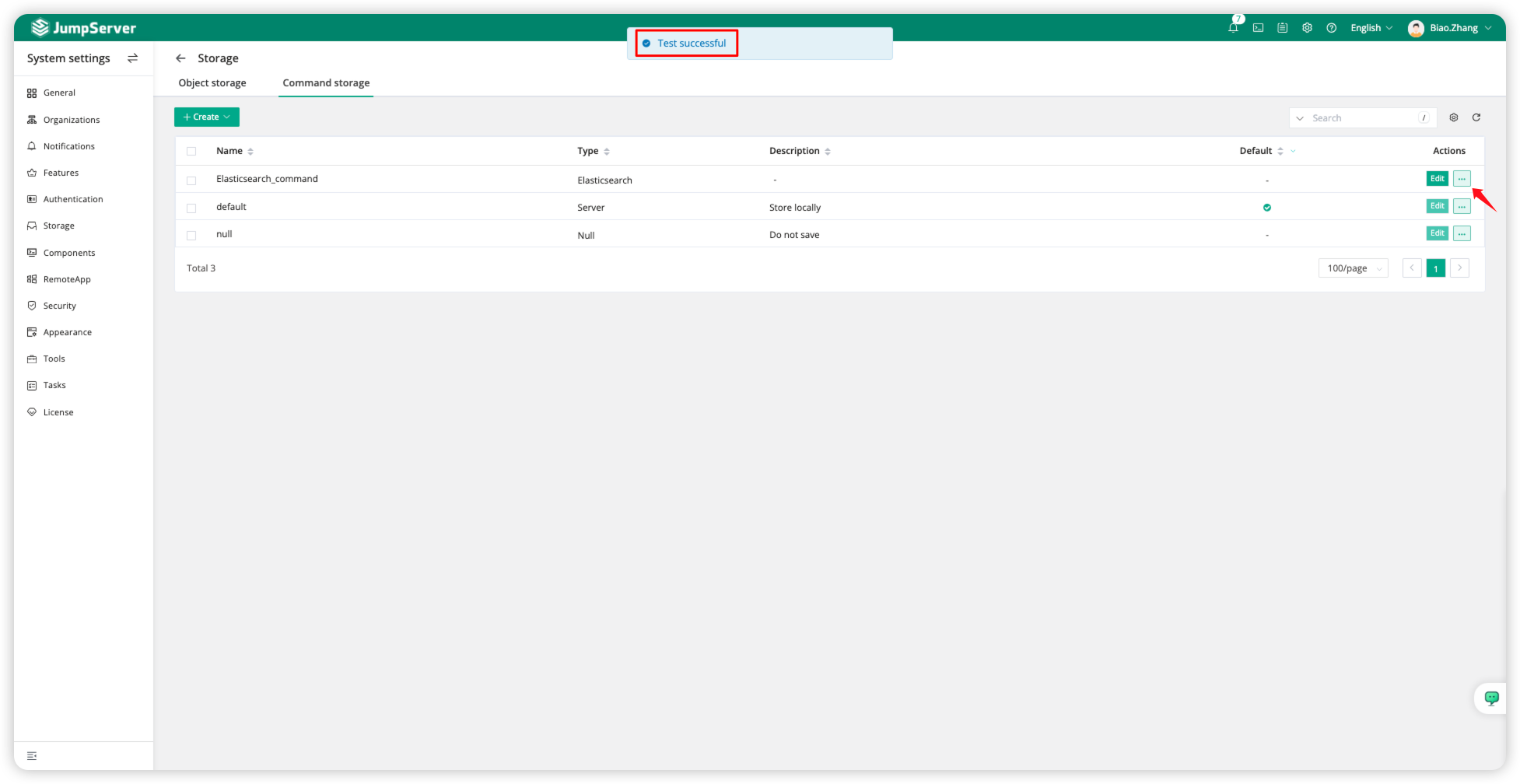
After successfully submitting the configuration, click the <···> next to the Elasticsearch type resource, then click <Test> to perform a connectivity test. If successful, it will return "Test successful."
Now let's apply the Elasticsearch service to the backend components of JumpServer.
Select all components, click <Actions>, then click <Update selected> to update <Command storage> to object storage, and confirm.
Function Verification
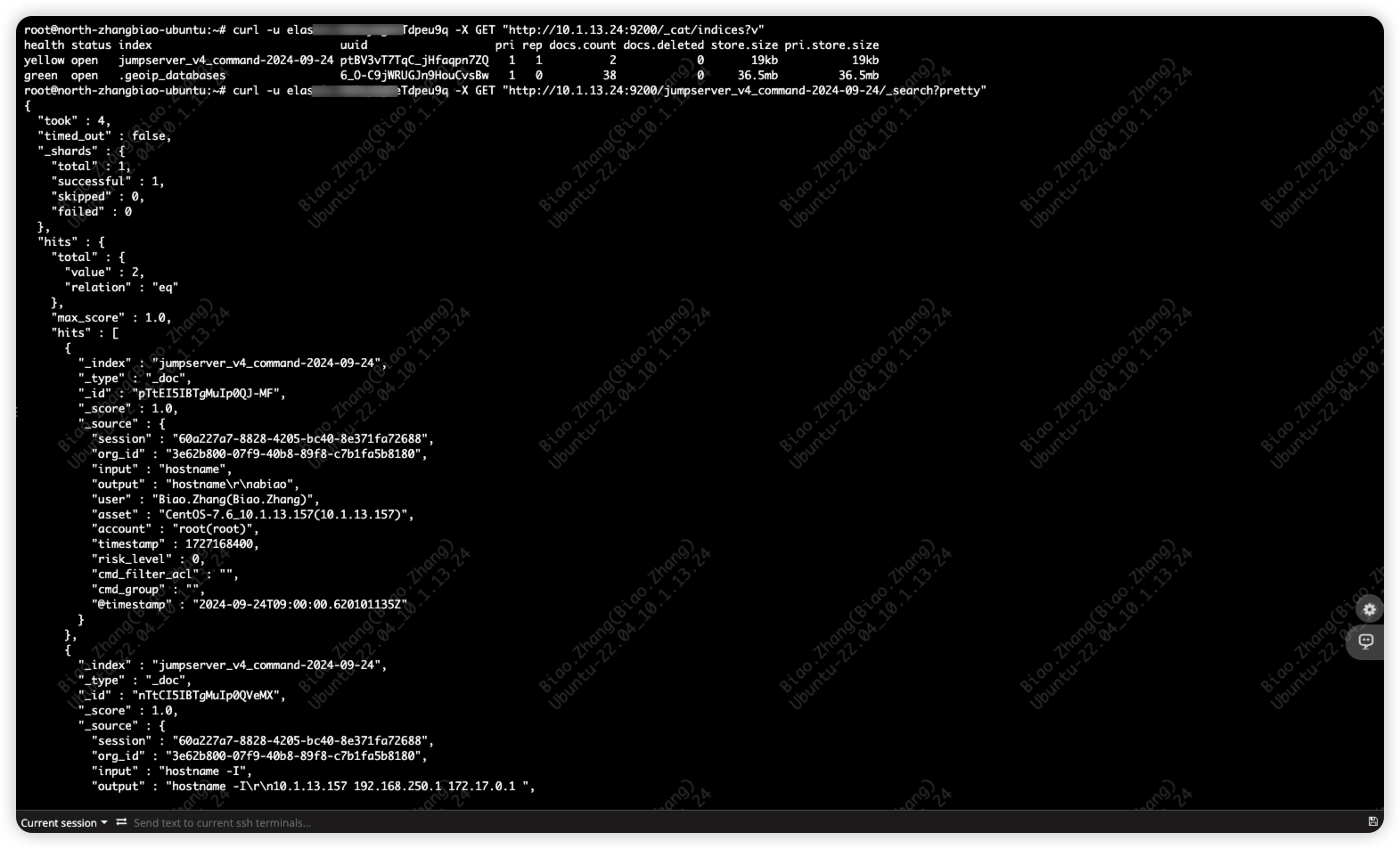
We switch to the <Audits> page of JumpServer and click on <Session commands>. We can see that the Elasticsearch service already exists in the Command storages on the left side. Then, we connect to the assets through the Web terminal, and the generated commands will be directly recorded in Elasticsearch.
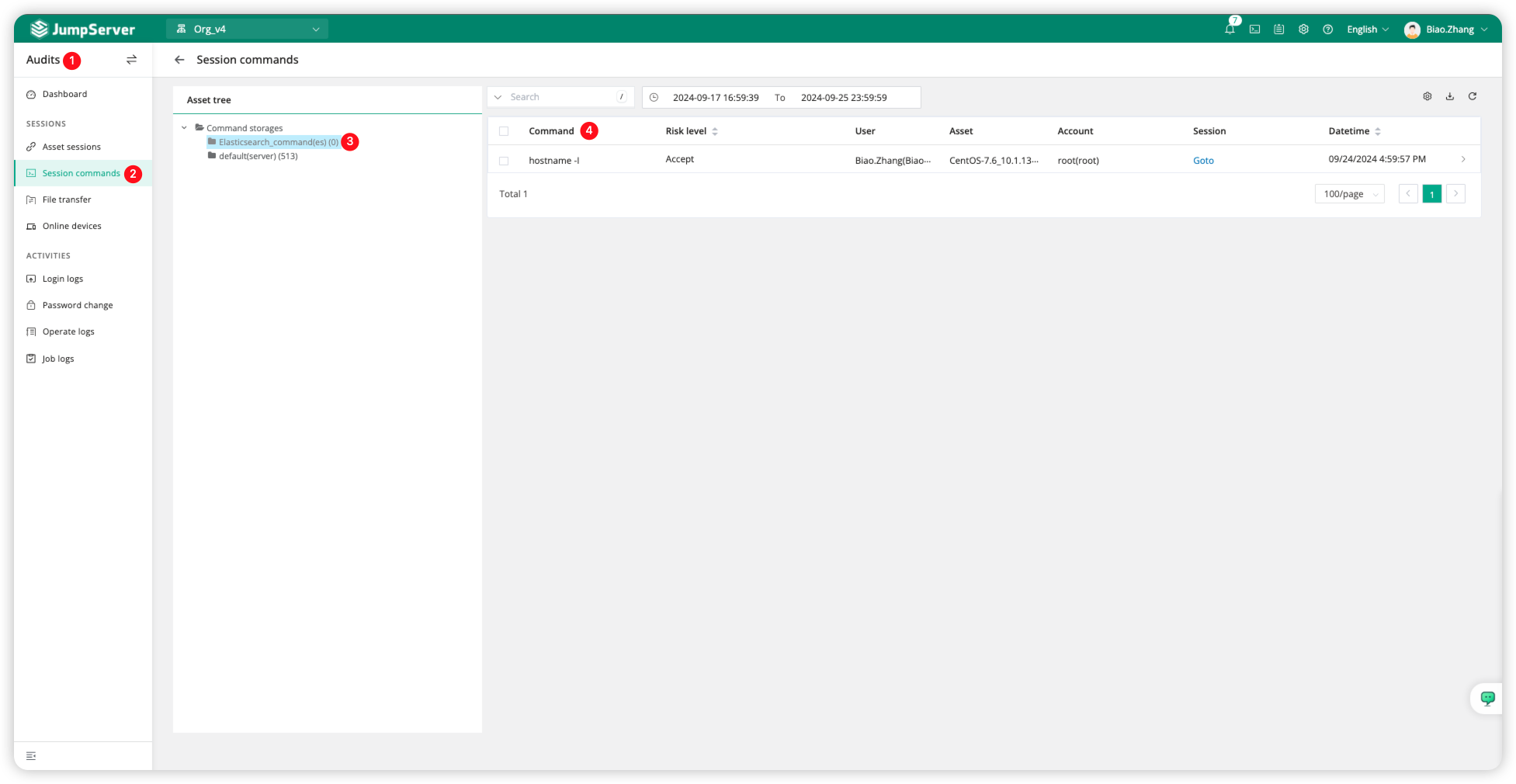
You can also directly go to Elasticsearch for query validation.