Preface
Currently, Jumpserver supports the following deployment solutions:
• Standalone Deployment
• High Availability Deployment
• Cluster Deployment
• Distributed Deployment
However, many users are unclear about which JumpServer deployment solution should be adopted for specific scenarios, and what constitutes the best practice.
This article primarily focuses on different business scenarios encountered by enterprises, and provides a detailed description of how to select and implement the optimal JumpServer deployment solutions for each scenario.
1.1 Single-Node Deployment
The single-node deployment of JumpServer does not simply refer to deploying on a single machine but rather encompasses the deployment of all three major components as single nodes (i.e., single-node components). Therefore, the single-node deployment of JumpServer can be categorized into two approaches: All In One and Independent Deployment, as illustrated in the following diagram:
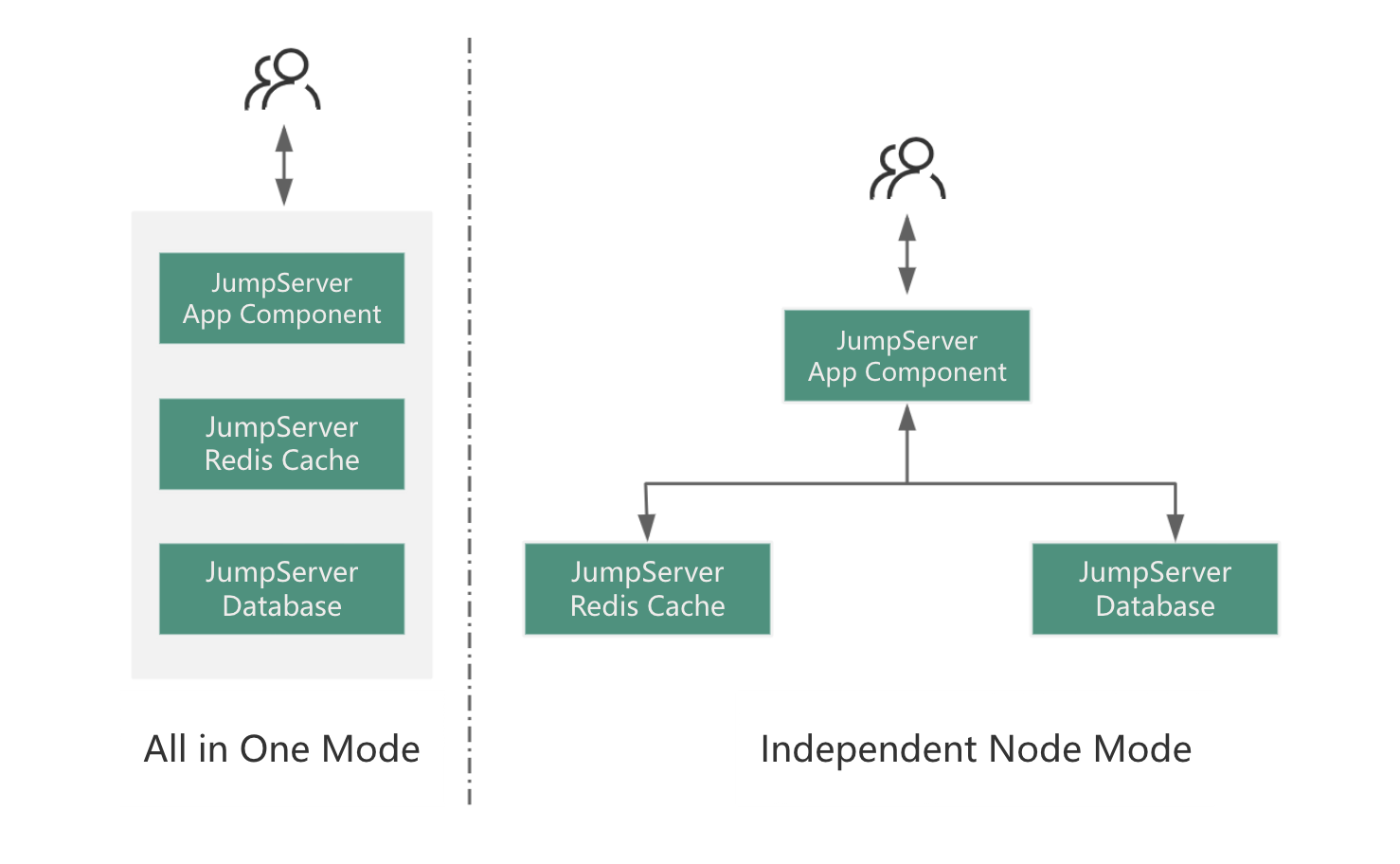
Whether to adopt a single-node deployment primarily depends on two factors:
The concurrent number of accessed assets, which refers to the number of simultaneous online sessions.
The total number of assets under management.
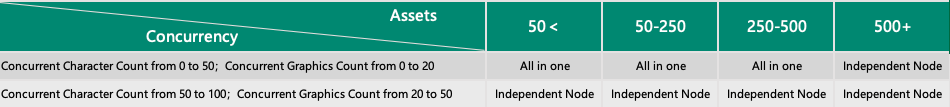
Recommended scenarios for single machine deployment:
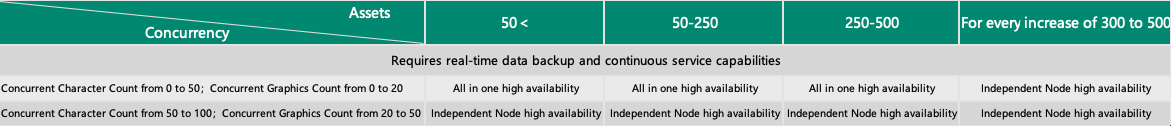
1.2 High Availability Deployment
Similar to single-node deployment, high availability deployment can also be divided into two main categories: All-in-One high availability and independent node high availability, as illustrated in the following diagram:
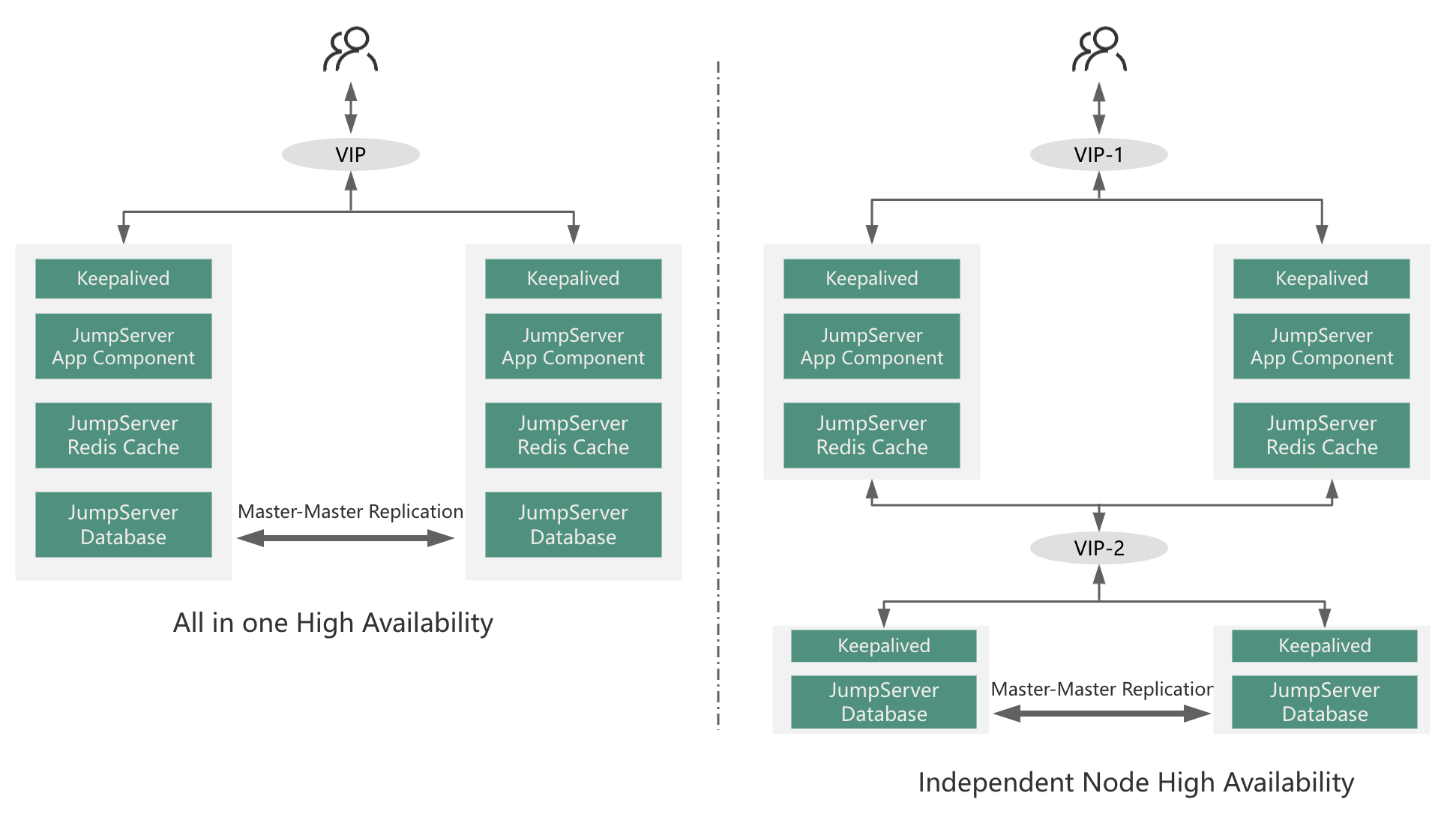
The essential difference between high availability deployment and single-node deployment lies in the differing requirements for data integrity and service continuity. High availability deployment can fulfill the following two enterprise needs that are beyond the capabilities of single-node deployment:
Real-time backup of database data and recording data.
Continuous service provision, with the ability to immediately switch to a backup node to continue service when the primary node encounters issues.
High Availability Deployment Recommended Scenarios Table:
1.3 Cluster Deployment Scenarios
The cluster deployment of JumpServer is primarily utilized in scenarios with high concurrency of asset access, with the objective of enhancing session processing capabilities.
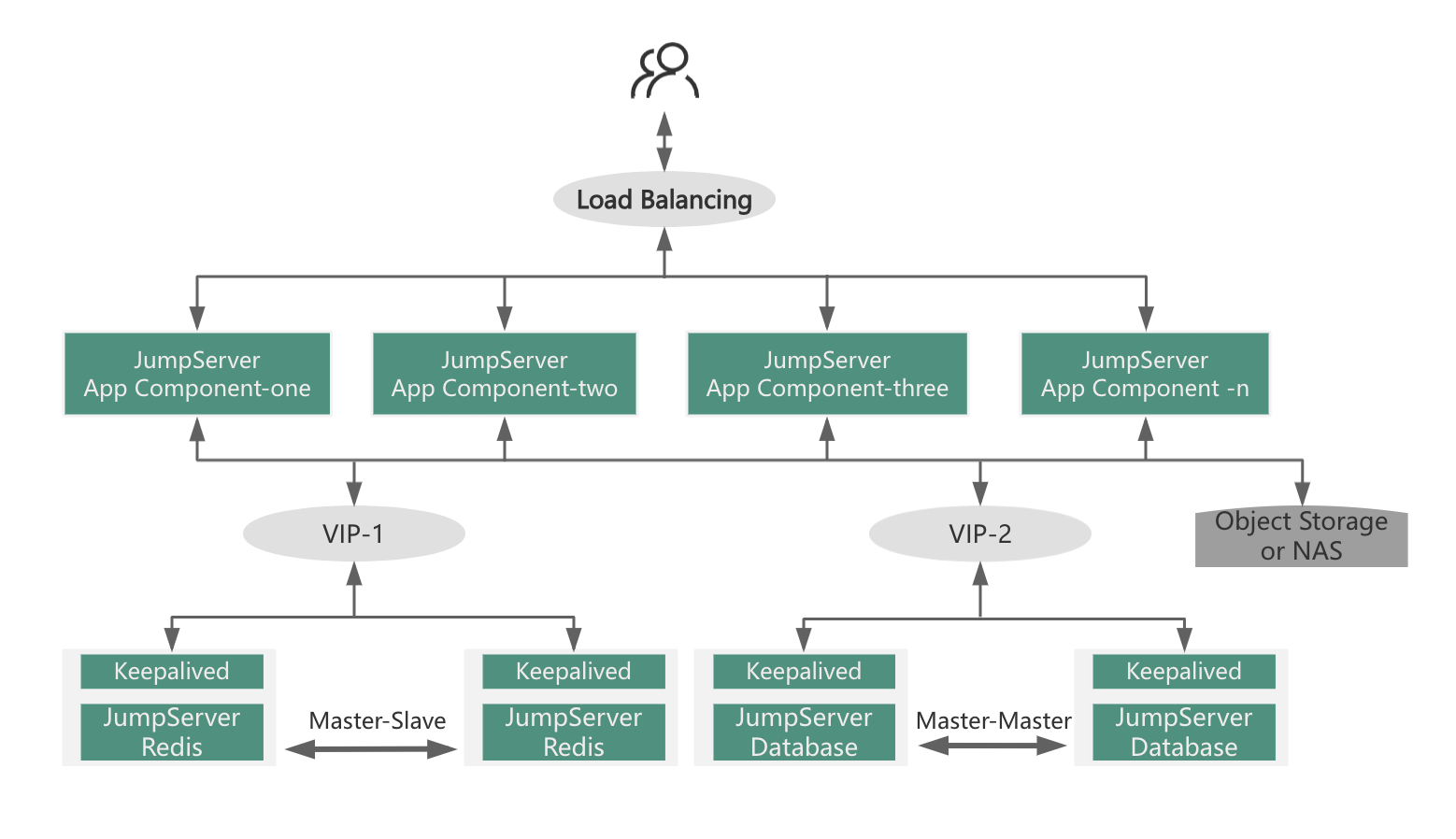
Cluster deployment also supports high availability for business operations, featuring the following characteristics:
Scenarios with a large number of assets and high concurrency of sessions (exceeding 200 character-based sessions and 100 graphical sessions concurrently).
Rapid growth in asset scale and concurrent session volume, requiring JumpServer's processing capacity to scale up quickly in response to the increasing asset scale.
Any node downtime does not affect the normal use of the platform, ensuring that business access remains normal with at least one available node.
The scale of the cluster can be dynamically expanded based on the increase in concurrent access sessions, independent of the number of assets. Therefore, the decision to adopt cluster deployment primarily depends on the concurrent number of access sessions.
Cluster Deployment Recommended Scenarios Table:

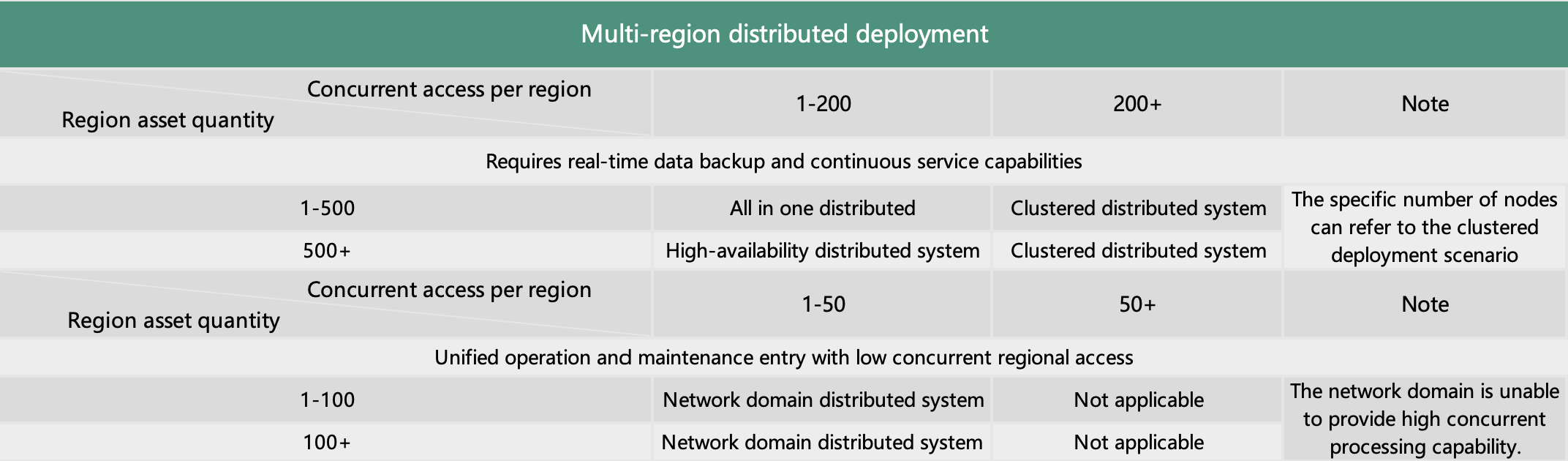
1.4 Distributed Deployment
The distributed deployment of JumpServer differs from other deployment scenarios. It is primarily used when assets are distributed across multiple geographical locations or network zones, and there are corresponding requirements for accessing and maintaining operational entry points.
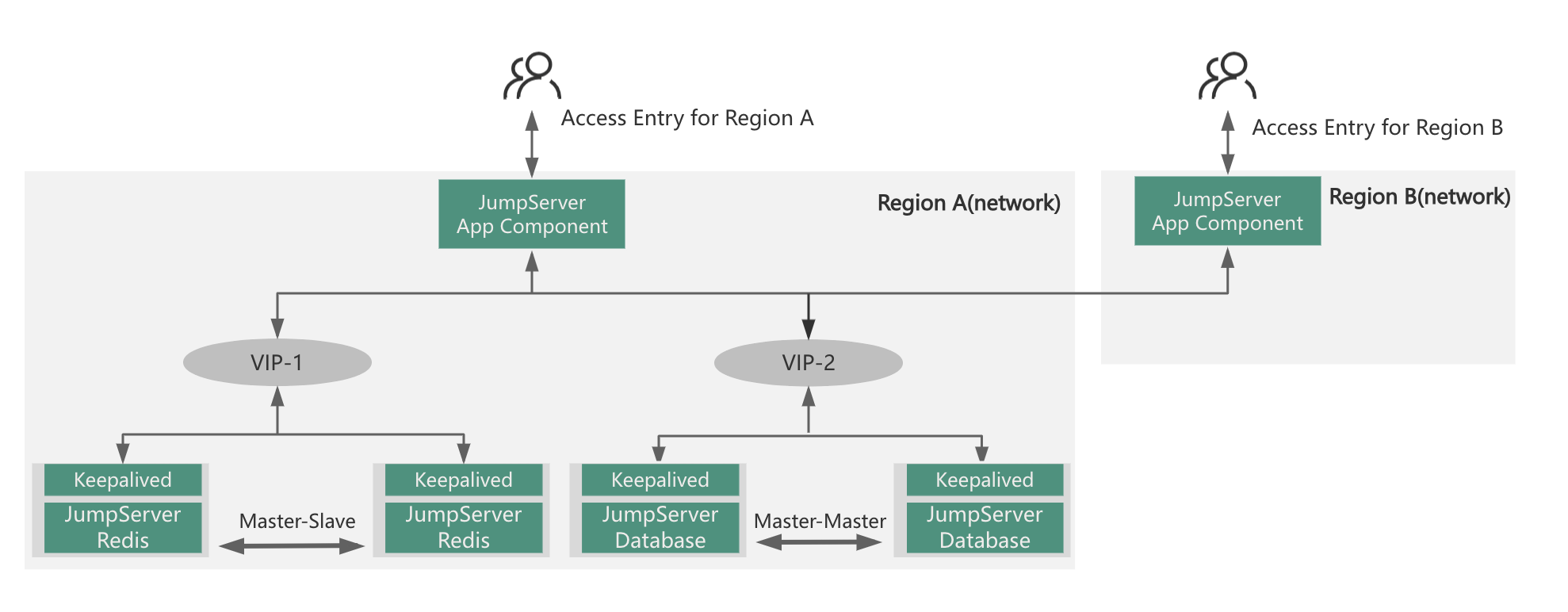
Translation of the Given Paragraph:
The distributed deployment of JumpServer boasts the following characteristics:
Assets belonging to users are dispersed across different regions (networks), necessitating unified management through the bastion host while enabling personnel in varying regions to access the bastion host locally for enhanced efficiency.
Assets, users, permissions, audits, etc., across different regions can be centrally configured and managed by administrators, or a multi-tenant model can be established by administrators to delegate management permissions and responsibilities.
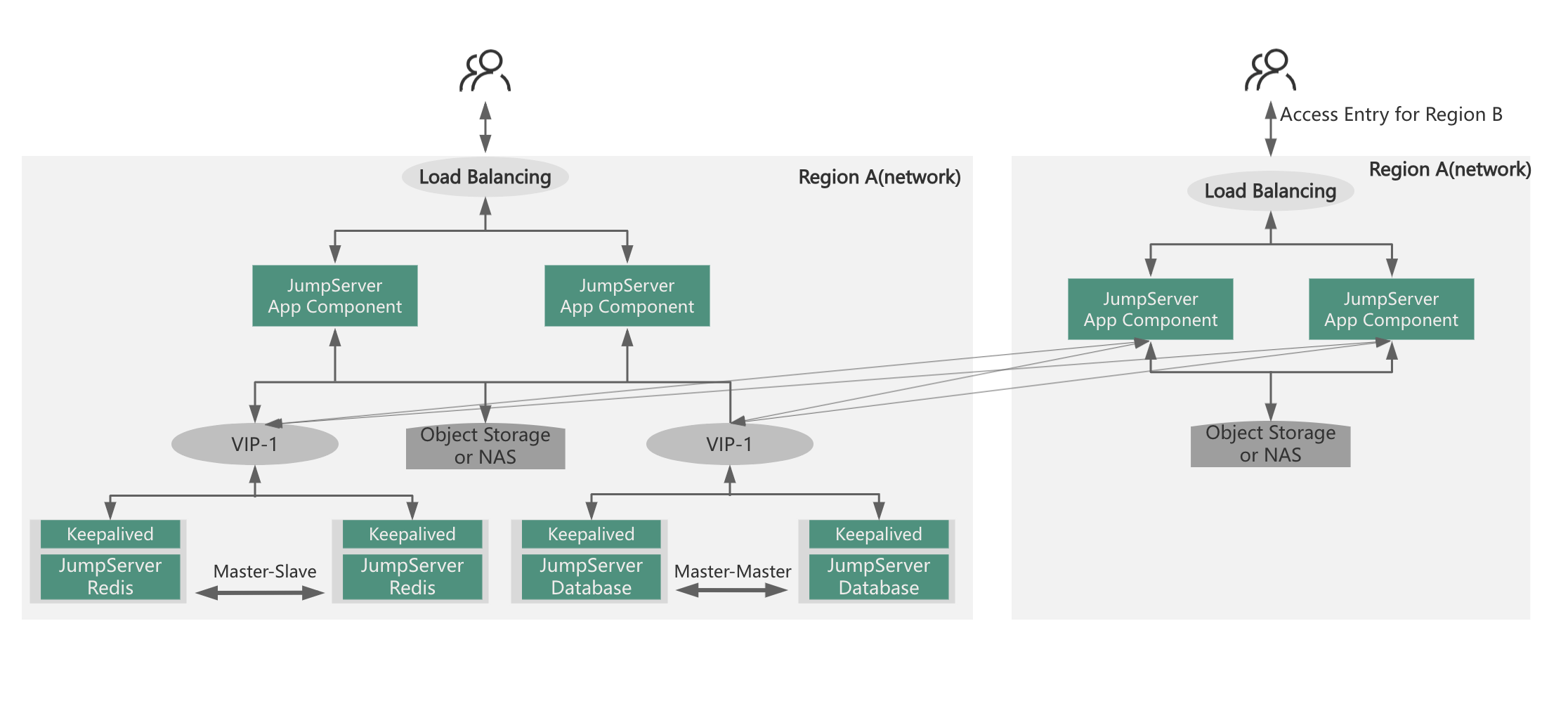
Naturally, if assets in different regions experience high concurrency or require business continuity, the distributed deployment can be extended to a cluster-based distributed deployment or a high availability distributed deployment. As follows:
The JumpServer domain-based distributed approach differs from the aforementioned schemes, as it primarily focuses on providing a unified operational and maintenance entry point. If the regional access concurrency is not high and all personnel access the system centrally, the domain-based solution can be adopted.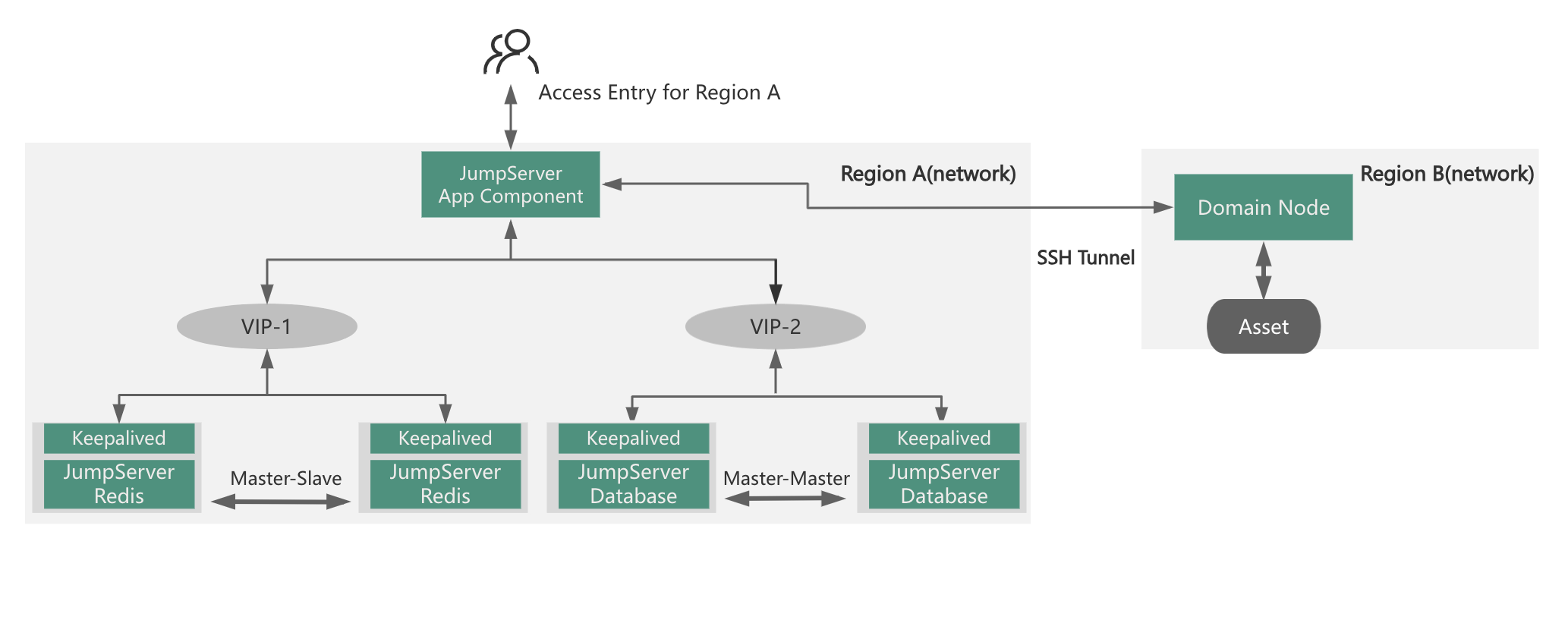
Distributed Deployment Recommended Scenarios Table: