1. User authority system
1.1 Organizational Structure
The Jumpserver Enterprise Edition provides multi-organization management capabilities. Each organization can be considered an independent organization team, and each organization team has independent user management and asset management capabilities. Organizations can have different roles such as organization administrators, organization users, and organization auditors. They can create their own assets and configure different asset permissions.
As shown below:
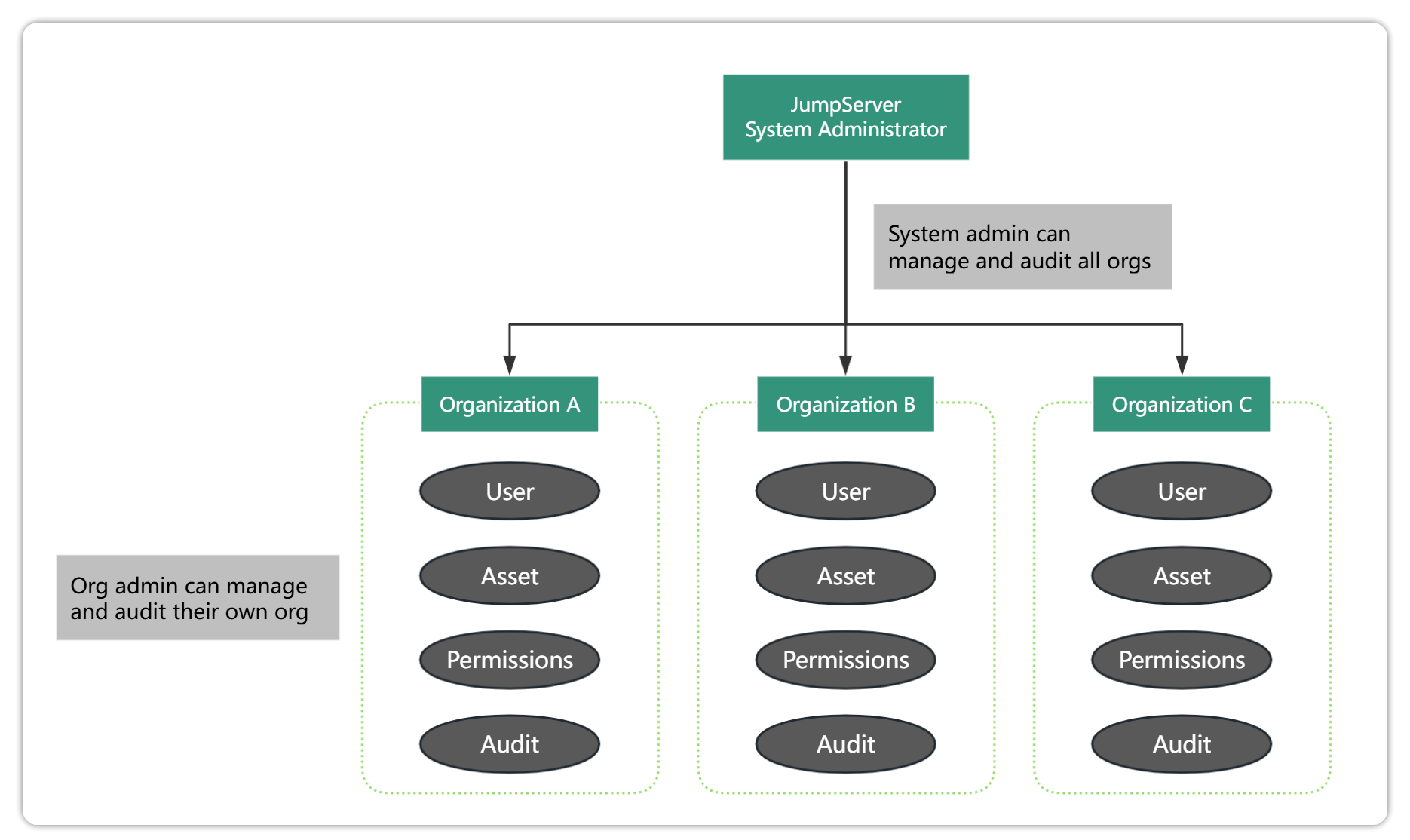
Take a large group as an example. This large enterprise is divided into the headquarters and Shanghai and Shenzhen branches in terms of IT management. Each branch has independent assets and users. From the perspective of the group headquarters, the headquarters and branches can be managed uniformly through the multi-organization capabilities of JumpServer, as shown in the following figure:
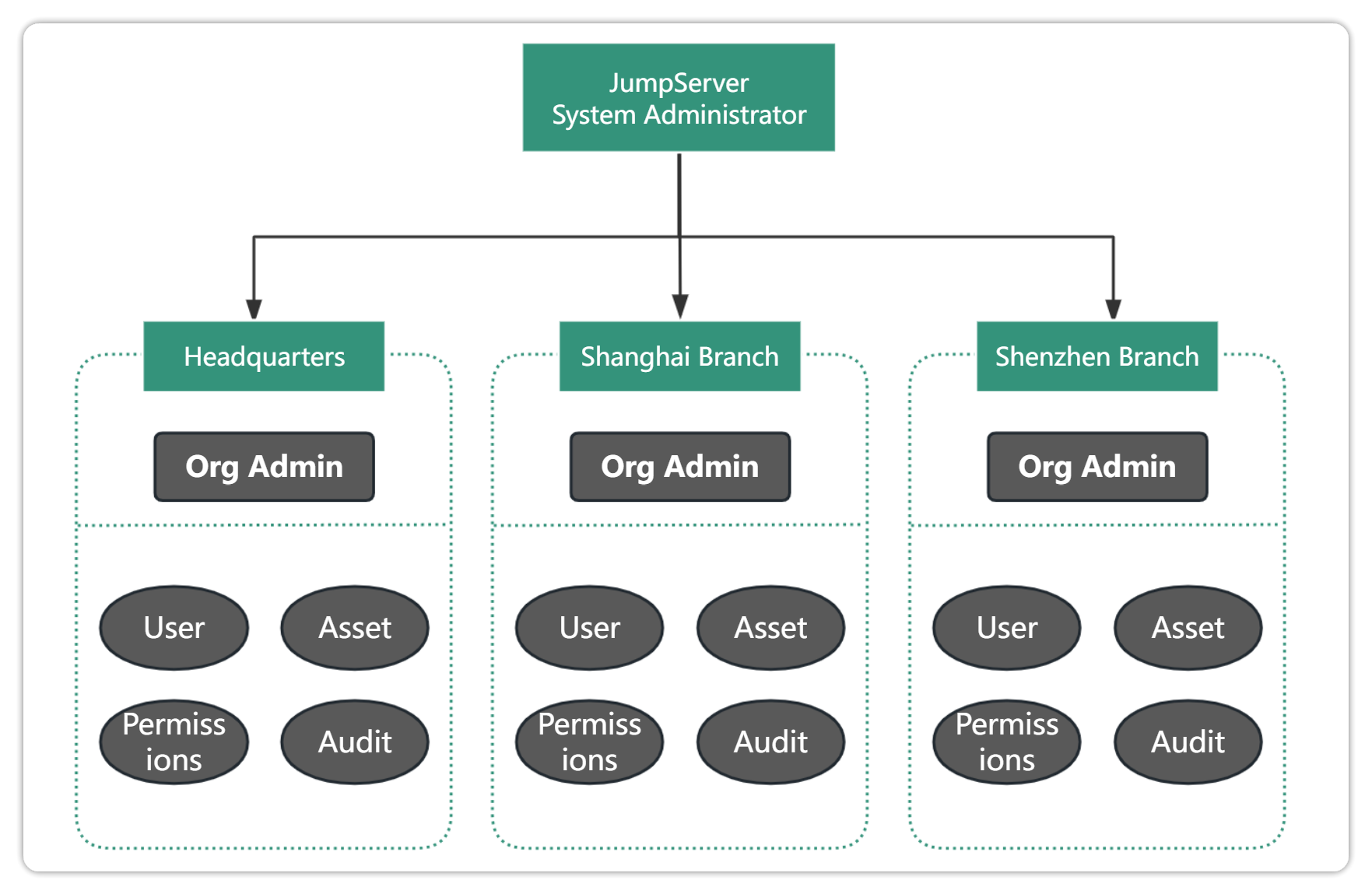
Note: The essence of JumpServer multi-organization is logical isolation of data, so it cannot solve the network connectivity problems of different regions or computer rooms. It is necessary to combine the distributed deployment capabilities of JumpServer to solve regional network problems under multiple organizations.
1.2 Role Relationship and Role Division
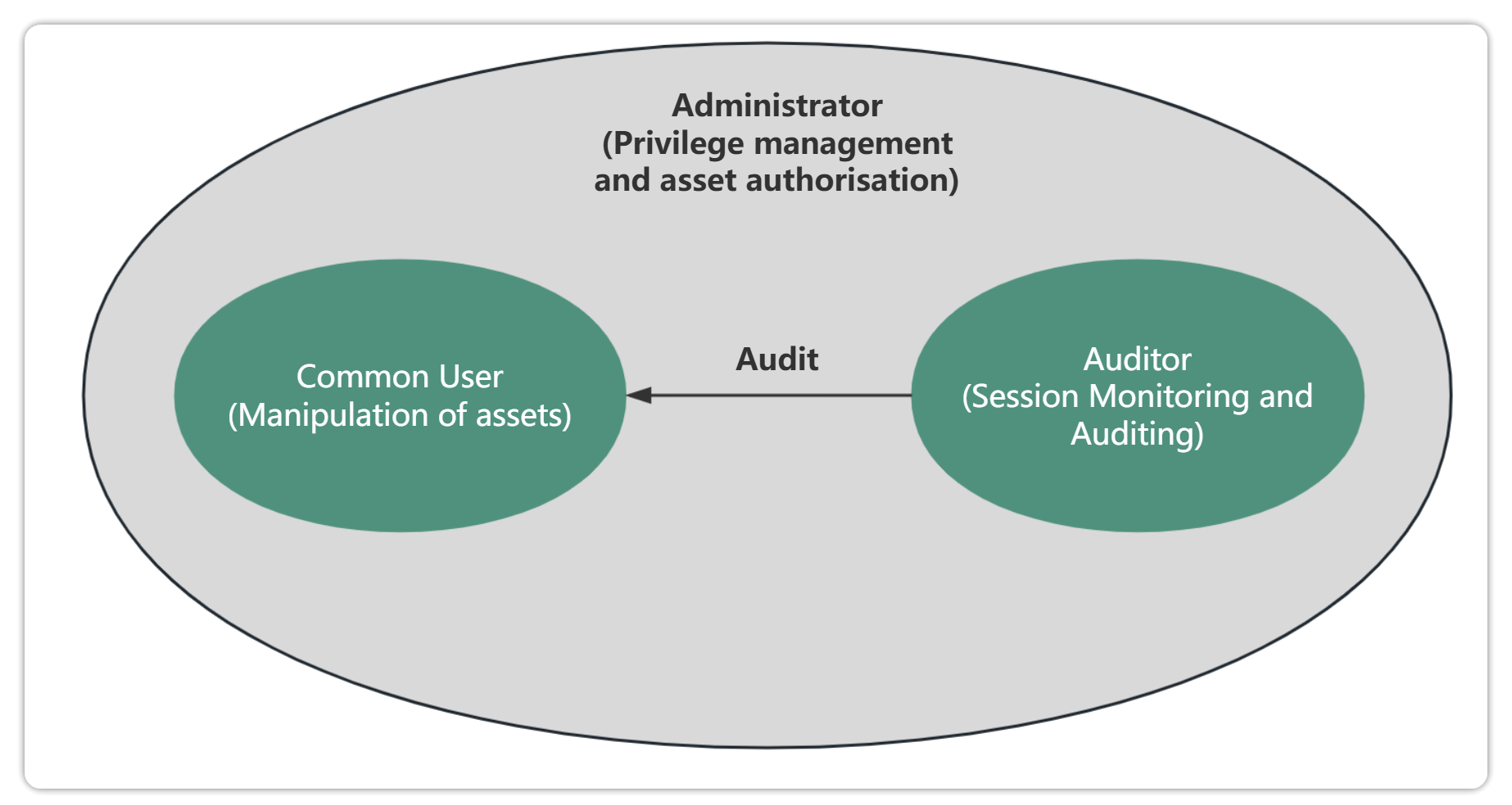
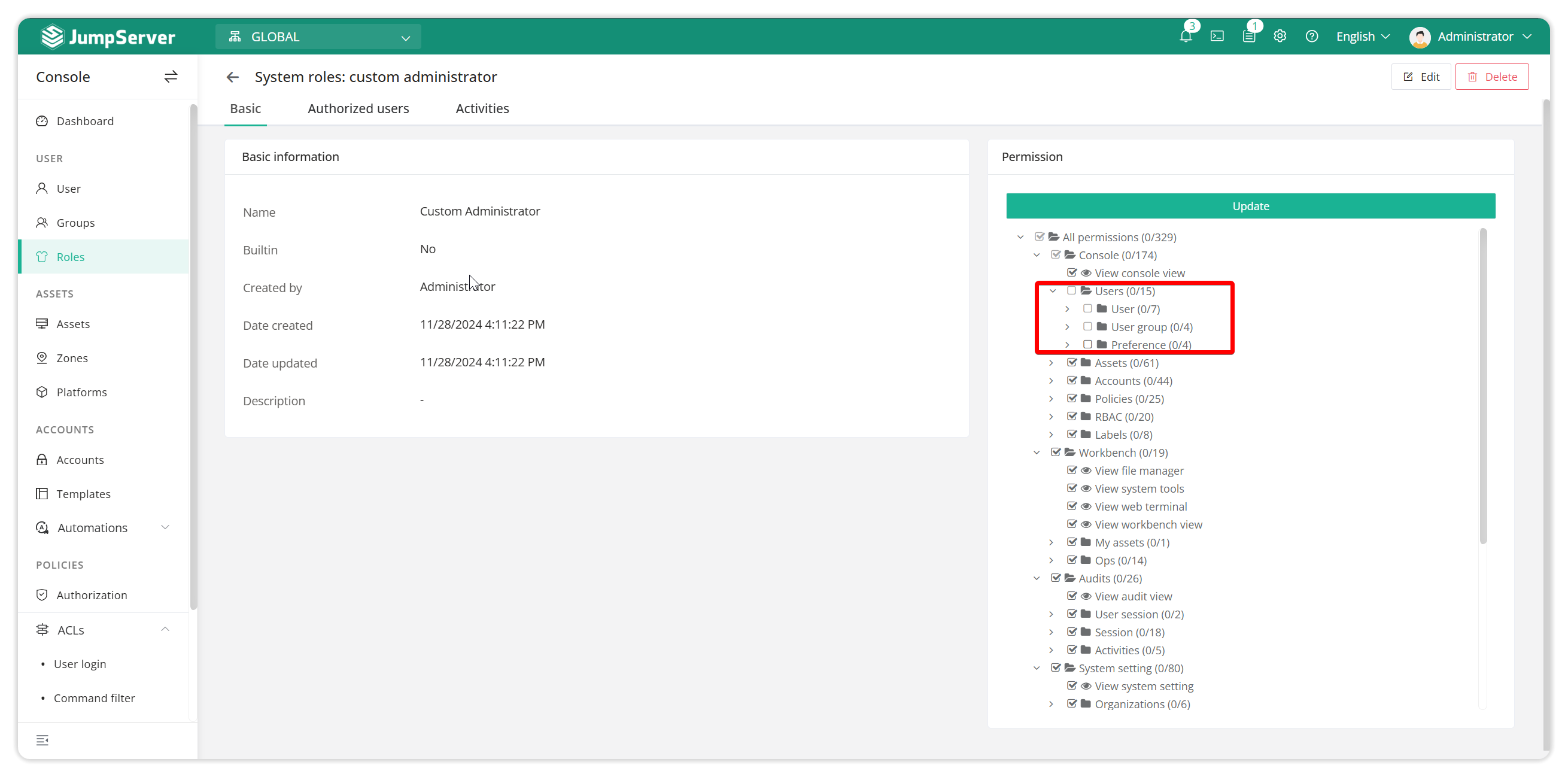
Jumpserver comes with multiple roles by default, such as system administrator, system auditor, user, etc. Each role has different management permissions. As an administrator, you can customize user roles according to actual needs and customize and edit user roles.
administrator: An administrator is a user who has all the permissions of the bastion host. As an administrator, you need to complete the approval of work orders, user authorization application, user permission changes, user locks, and other operations. At the same time, you need to make corresponding permission changes to the roles and permissions of employees according to changes in their positions.
Auditor: Auditors can view the current user's operation behavior, user permissions, user information, file transfer records, user operation logs, etc. When a user triggers a dangerous command, the auditor can conduct an investigation on the user's operation.LineReal-time monitoring to detect illegal operations.StandingStop the user's operation.
Normal User: Ordinary users have normal operation and asset login permissions, but cannot modify configurations.
Custom user roles:
1.3 Relationship between users and asset accounts
In JumpServer, the user's operation rights on assets are authorized by the authorization rules.It is determined by the asset account. Generally, the business permissions are differentiated by the asset account, which is divided into three categories: readable account, writable account and high-authority account.
Then authorize the corresponding asset account according to the user's role and needs. The user can log in to the authorized asset through the authorized asset account. The relationship is as follows:
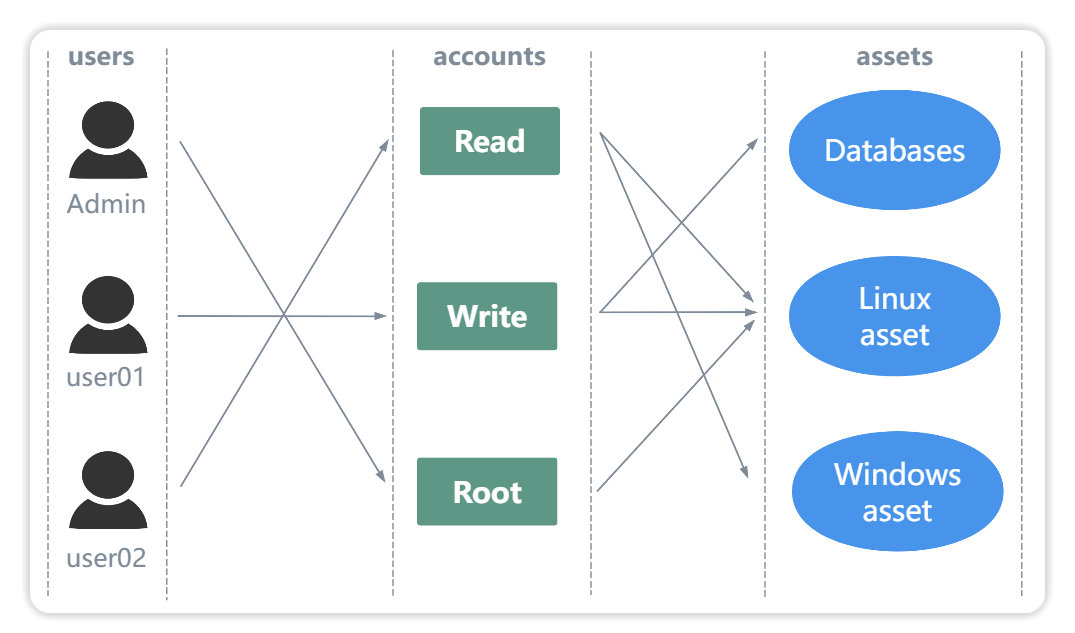
1.4 Asset Account Permission Control
The permissions of the asset account are also crucial, as they often determine the user's actual operating permissions on the server.
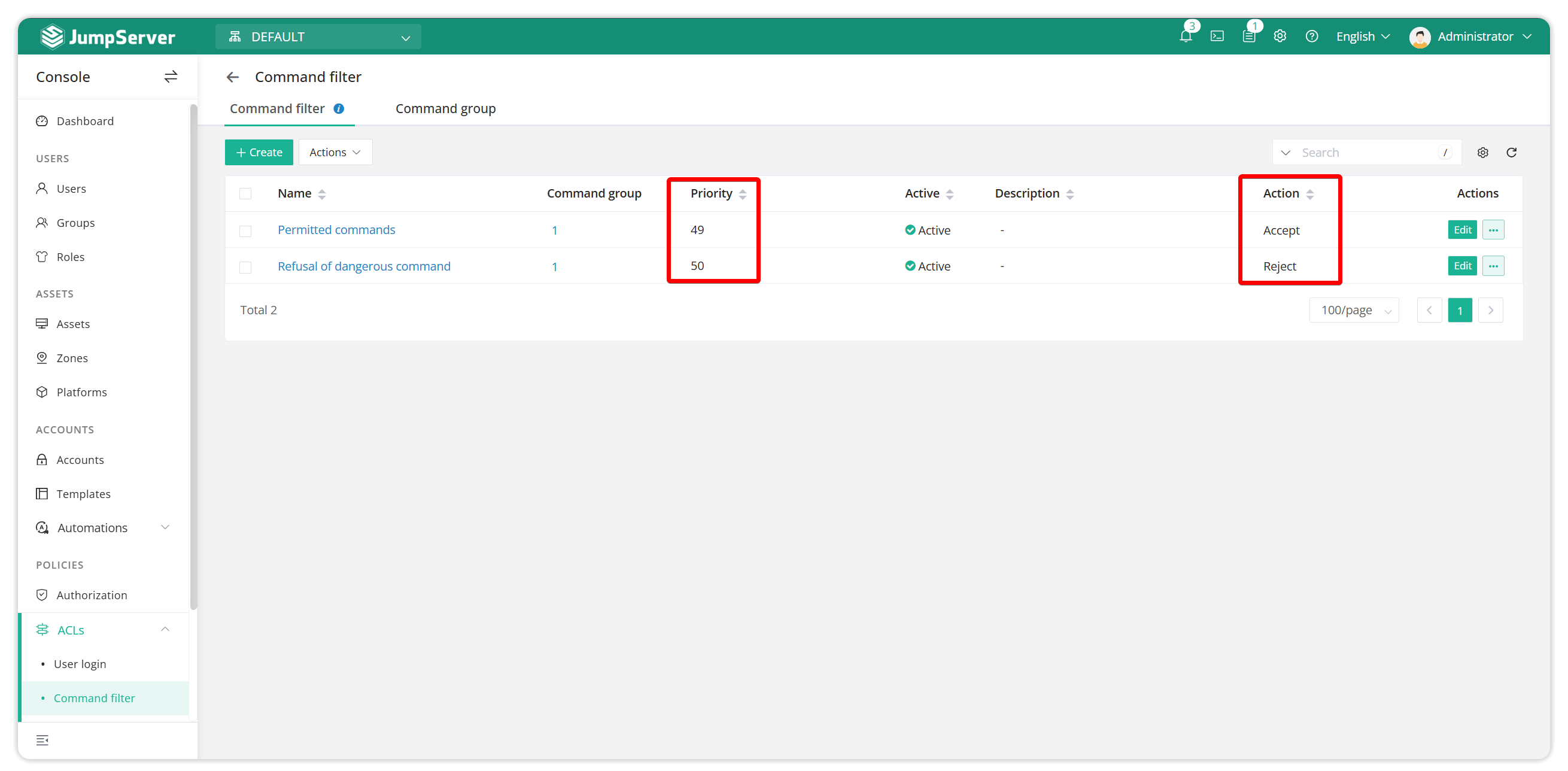
Through the command filtering function of jumpserver, you can filter the executed commands, filter high-risk commands, reduce operational risks, and perform operations such as permission, approval, rejection, and notification when the command is matched.
A command filter can be bound to multiple command groups. When the bound user uses the asset binding account to connect to the bound asset to execute a command, the command needs to be matched by all command groups bound to the filter, and the command with the highest priority will be matched first.
1.4.1 Example usage scenarios
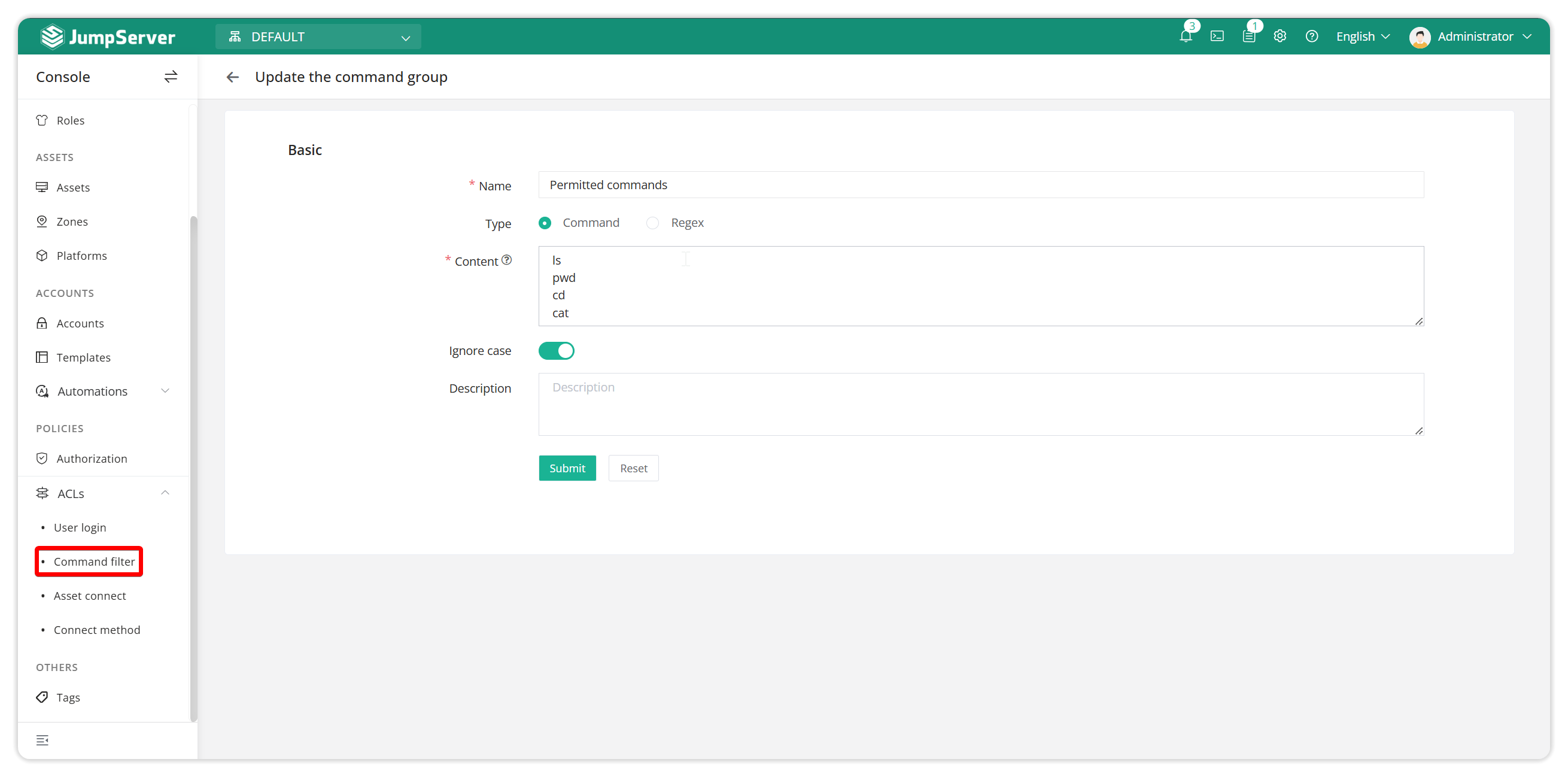
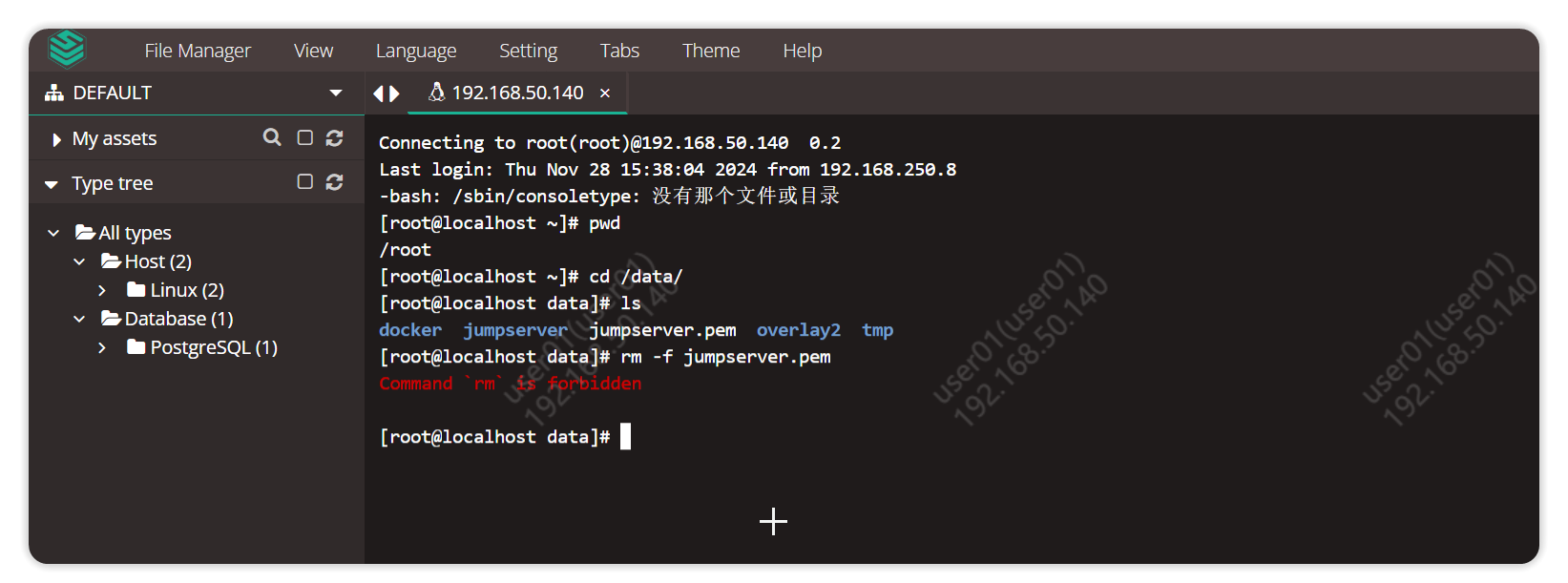
A user can only perform viewing operations (ls, pwd, cd, cat, less, more) on the group of assets, and other commands are prohibited.
1.4.1.1 Creating a Command Group
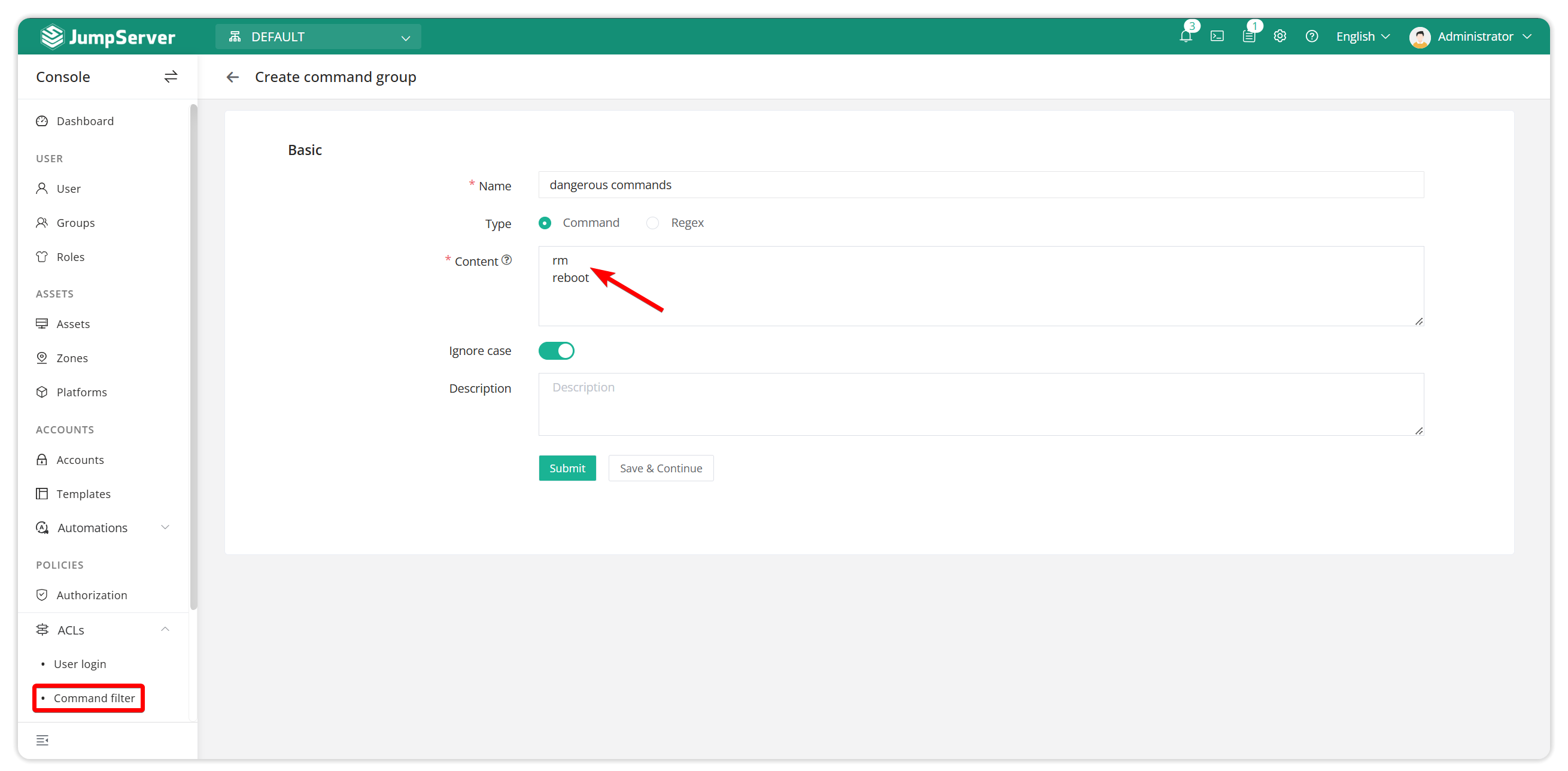
Command groups can be bound to command filters. Two types of command groups can be created in command groups: regular expressions and commands.
Command Group 1: Deny refusal of dangerous command
Command group 2: commands that are allowed to be executed.
1.4.1.2 Creating a command filter rule
Create two command filtering rules. The priority of the deny rule is higher than that of the allow rule. That is, the smaller the number, the higher the priority.
1.4.1.3 Verification
2. Enhanced user login security
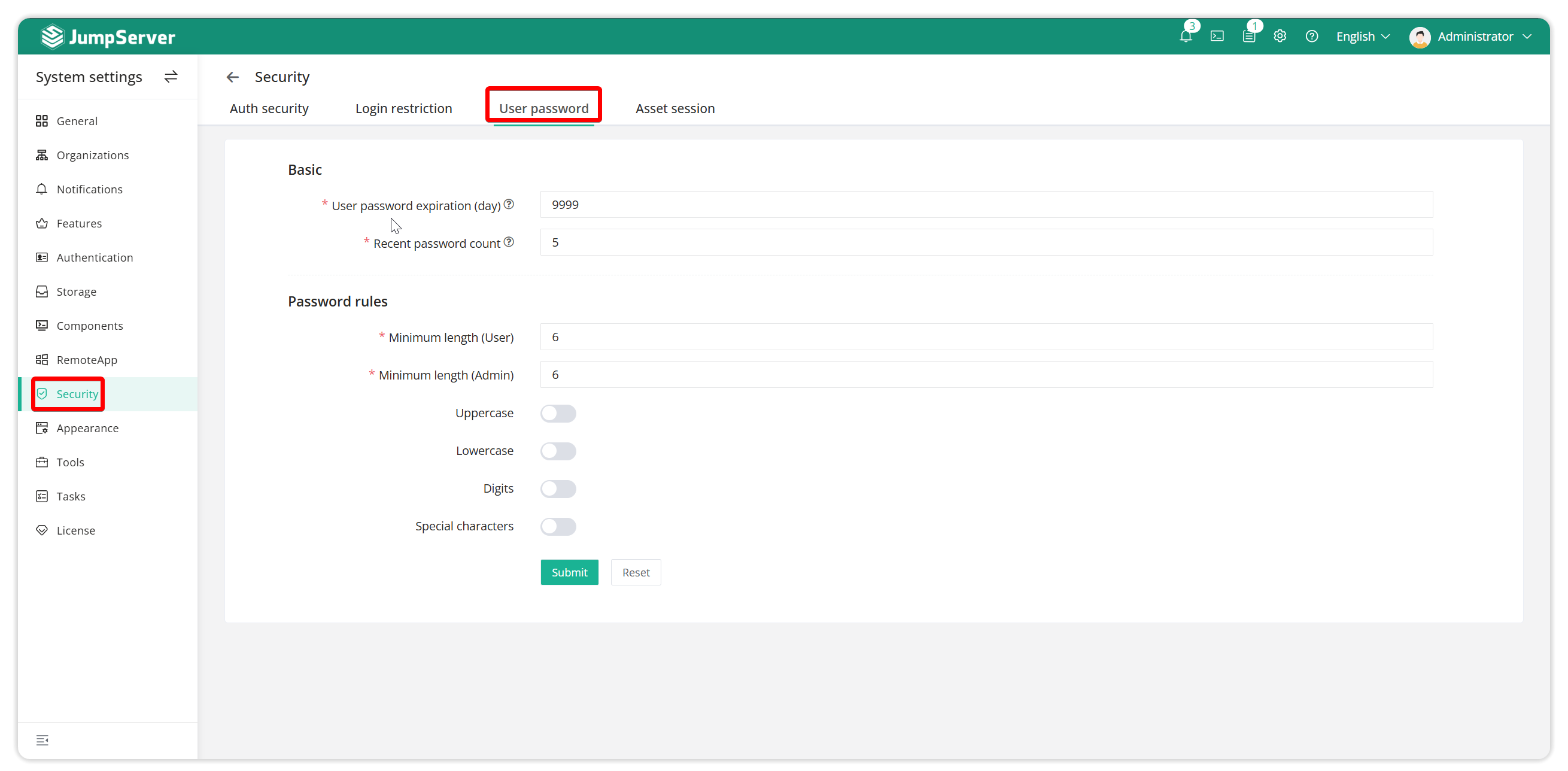
2.1 User password complexity
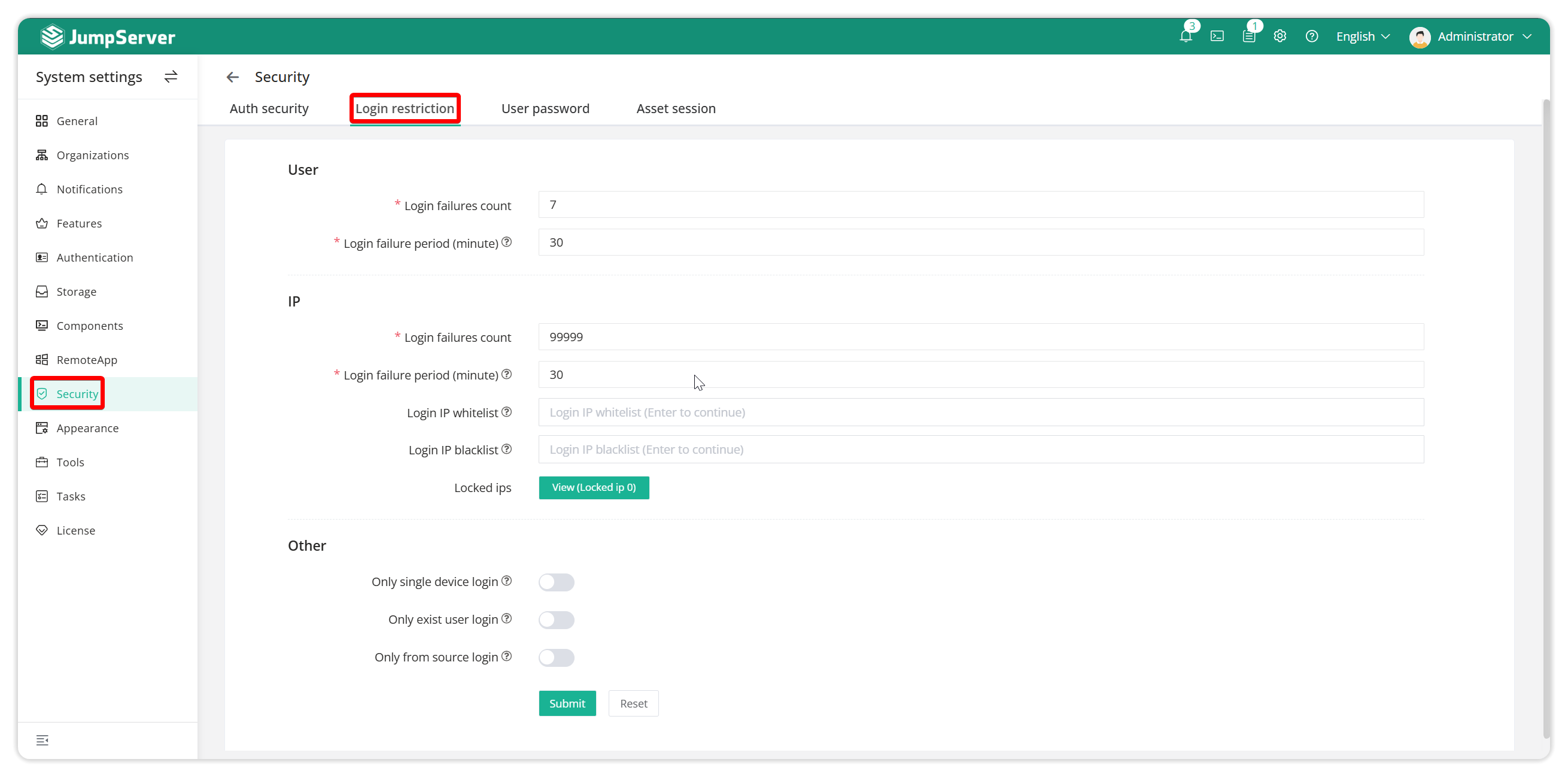
2.2 User login restrictions
User login restrictions can be set based on user or IP or user's IP. According to the user login Jumpserver limit set by the user, how long it takes for the user to log in again after exceeding the number of incorrect login attempts.
Parameter Description:
Limit the number of failed user login attempts: the maximum number of failed user login attempts with wrong passwords, after which the user will be locked out for a period of time.
Banning interval: the time when the user is locked out.
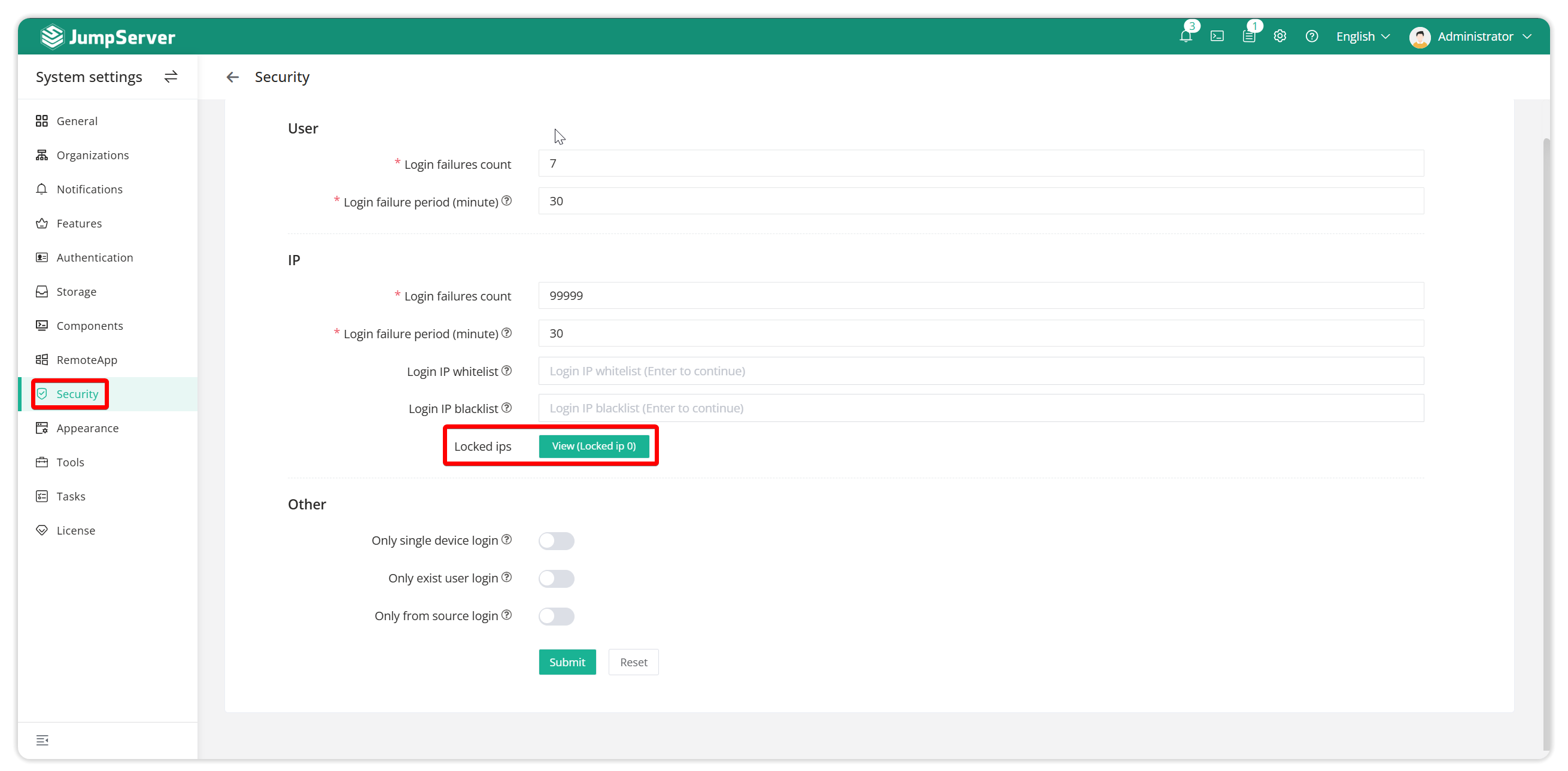
Limit IP Login Failures: Maximum number of failed login attempts for an IP, after which it will be banned for a period of time.
Ban IP login interval: the time of IP locking.
IP Login Whitelist: IPs allowed to log in to the bastion.
IP Login Blacklist: IPs that are not allowed to login the bastion.
Locked IPs: IPs that have been locked after exceeding the set number of login failures.
Only One Device Login: Allow users to login on only one device. The next device logged in, the previous logged in device will be forced offline.
Only Existing User Login: Only allow users that exist in JumpServer user list to login.
Login from user source only: Allow users to login only from the source listed in the user list.
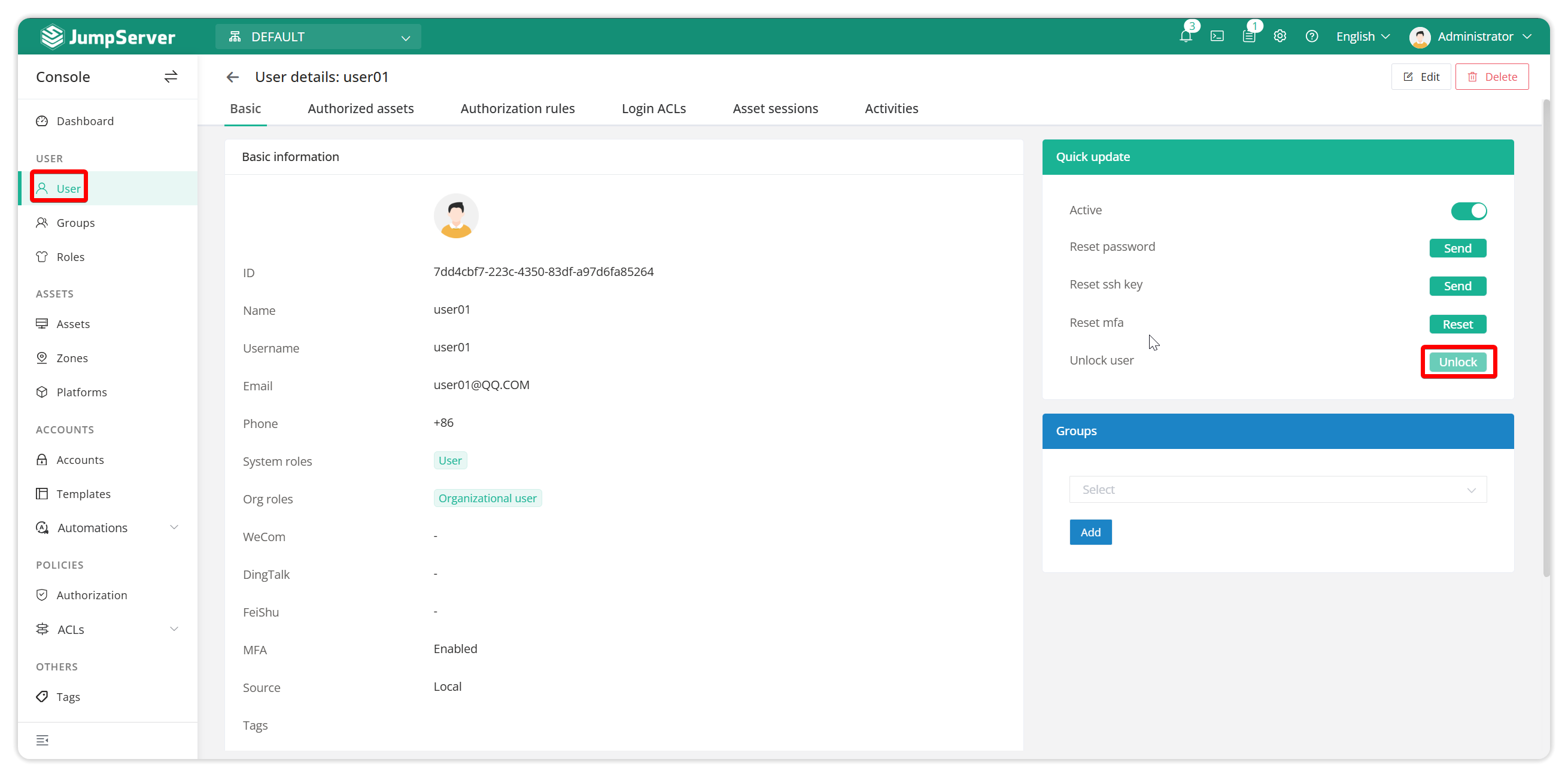
2.3 How to unlock a user
If the user is locked out, you can also contact the administrator to unlock it manually.
2.4 Two-factor authentication
User login restrictions can enable two-factor authentication for more secure login to JumpServer.Currently, JumpAerver supports two types of two-factor authentication: MFA two-factor authentication and SMS authentication.
2.4.1 MFA two-factor authentication
In System Settings - Security Settings - Authentication Security, set up global MFA authentication and implement MFA authentication for third-party login users.
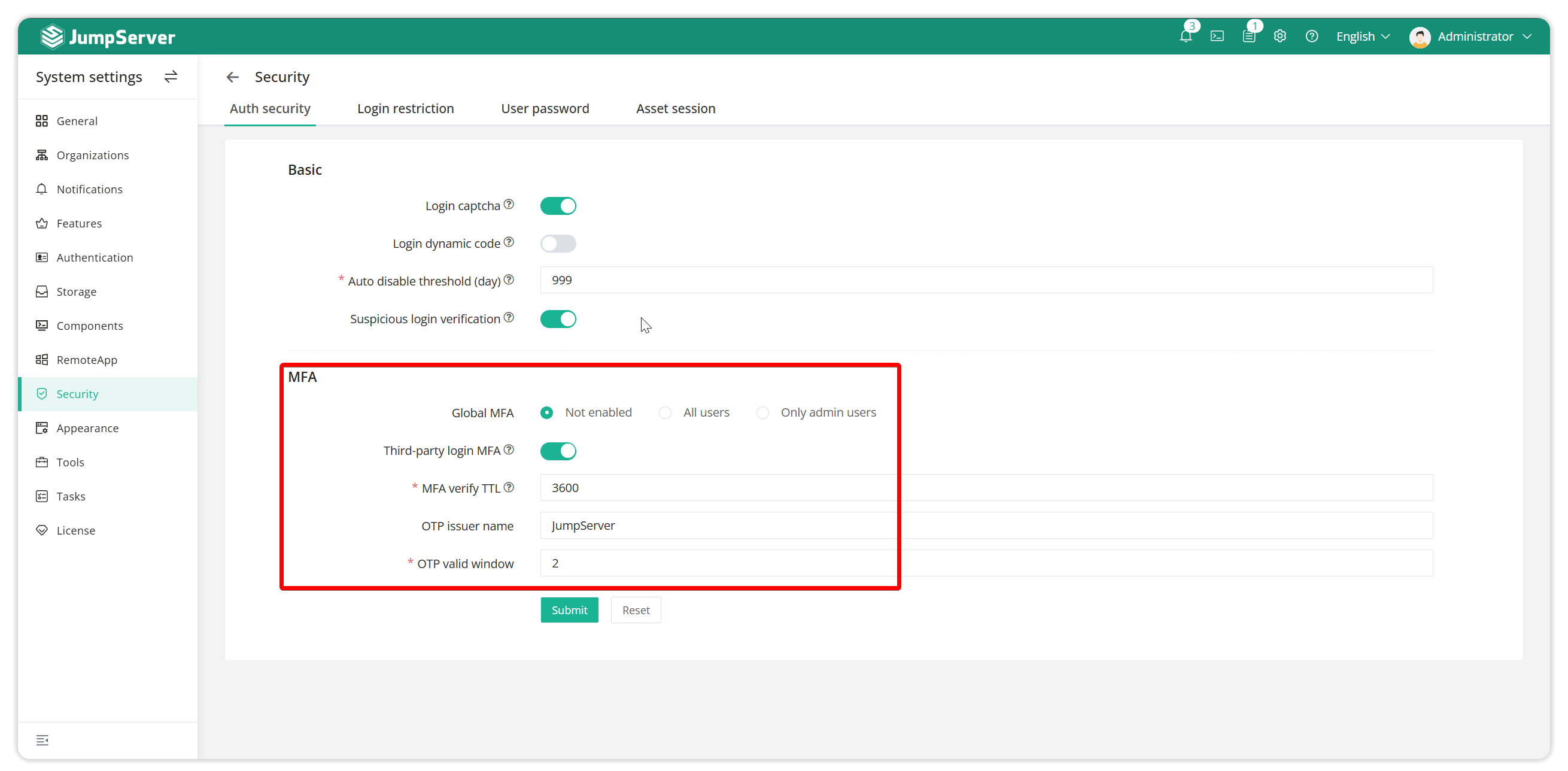
Without enabling global MFA, you can choose to enable MFA two-factor authentication for a single user when creating a user.
Note: The global MFA enable rule takes precedence over the MFA disable rule for individual users.
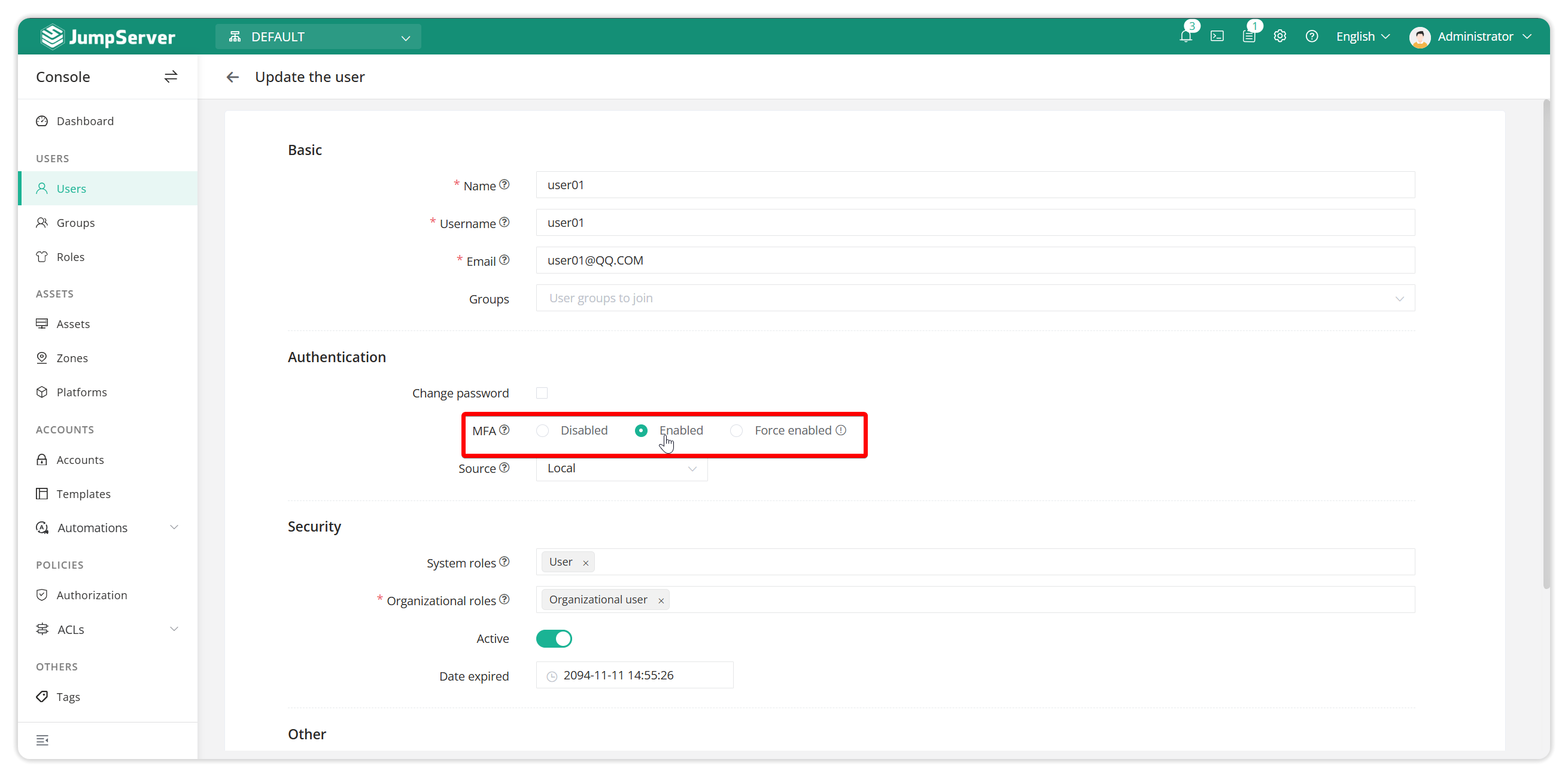
When a user logs in for the first time, they can bind MFA authentication, and when they log in for the second time, they can directly use MFA for login verification.
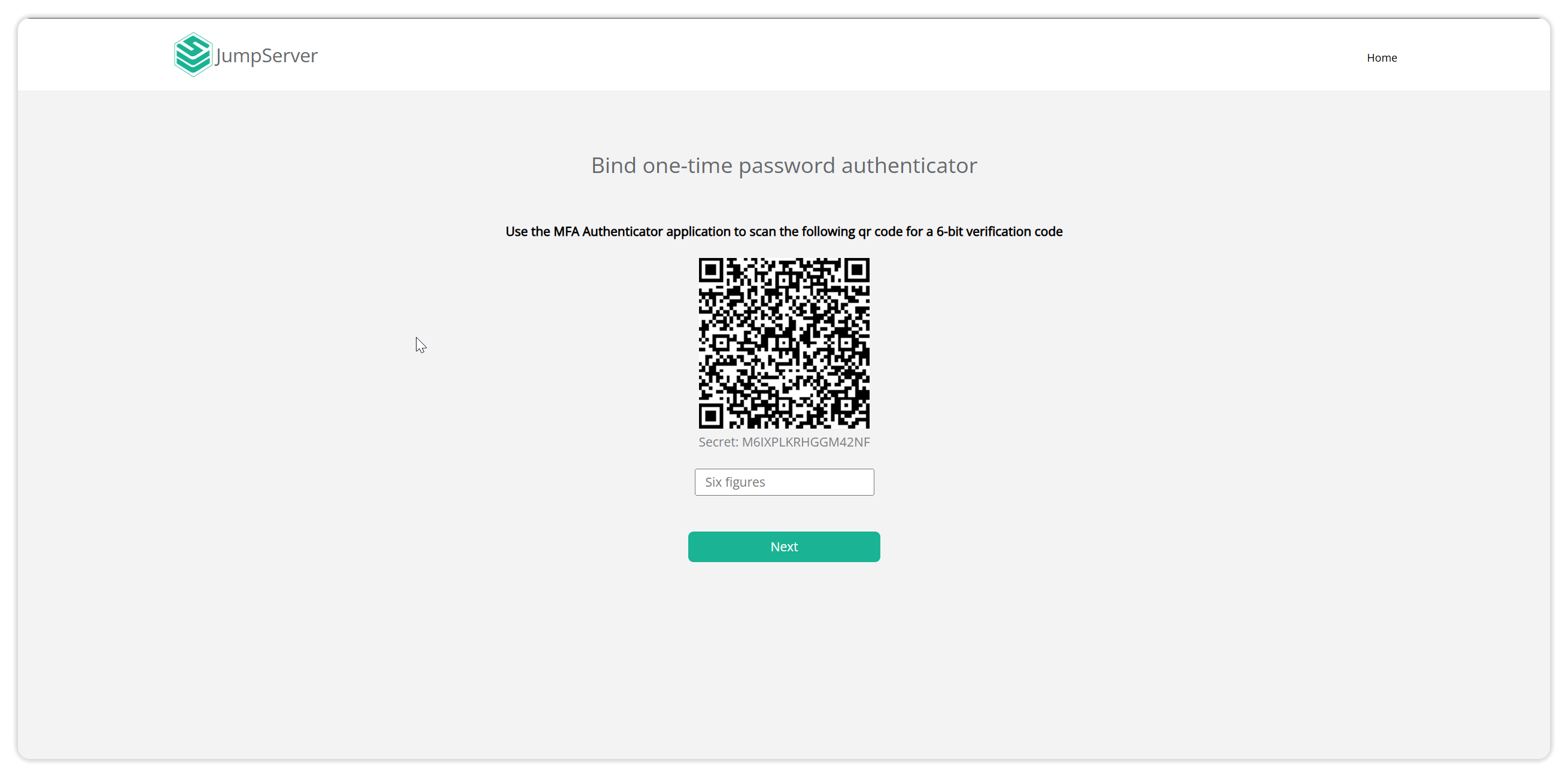
JumpServer commonly used MFA tools can be found at: https://kb.fit2cloud.com/?p=6
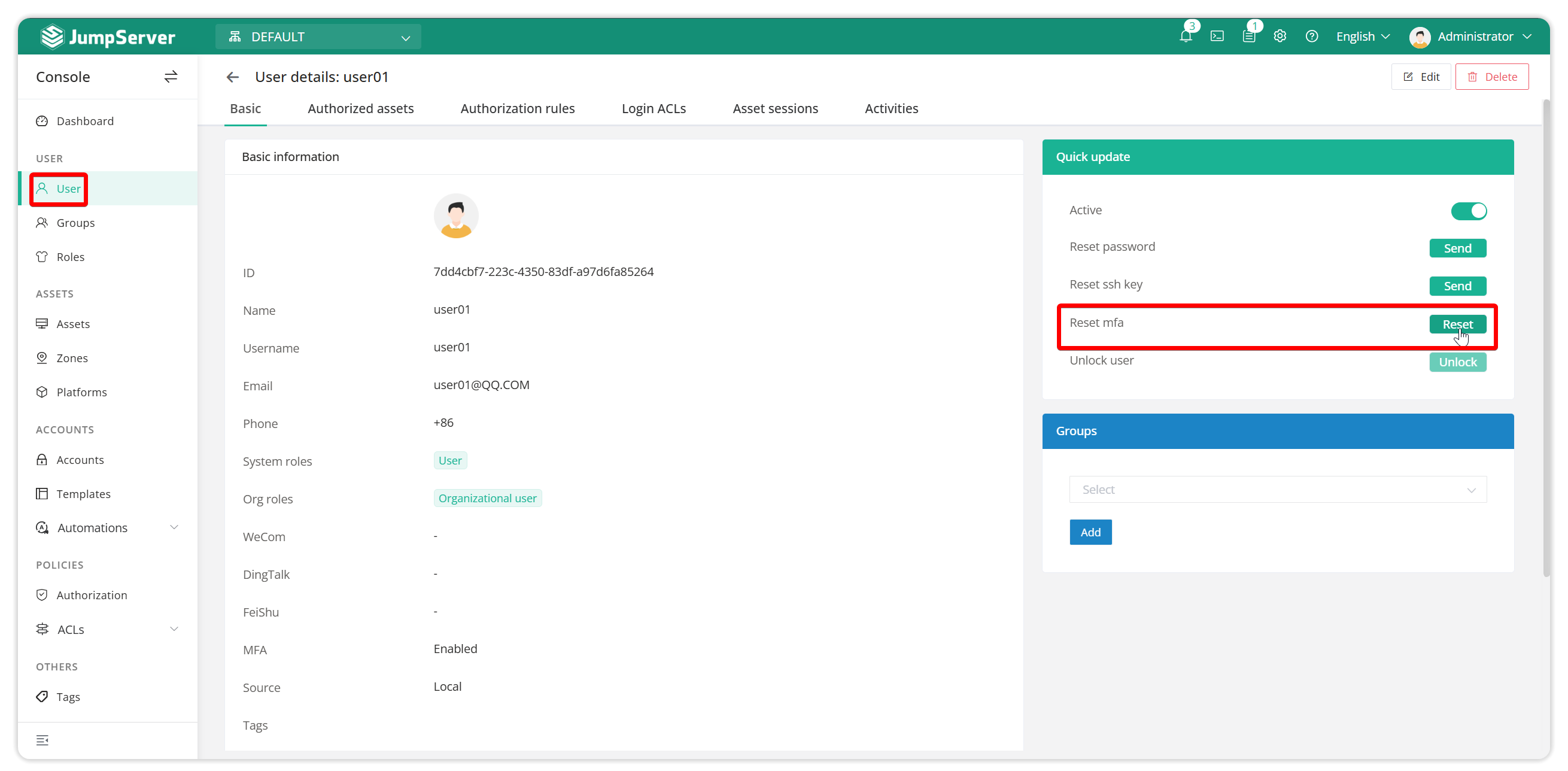
2.4.1.1 Reset MFA
If a user changes to a new device and cannot obtain the MFA verification code of the previous device, the user can contact the administrator to reset the user's MFA. The user can use the new device to scan the code again to bind the MFA.
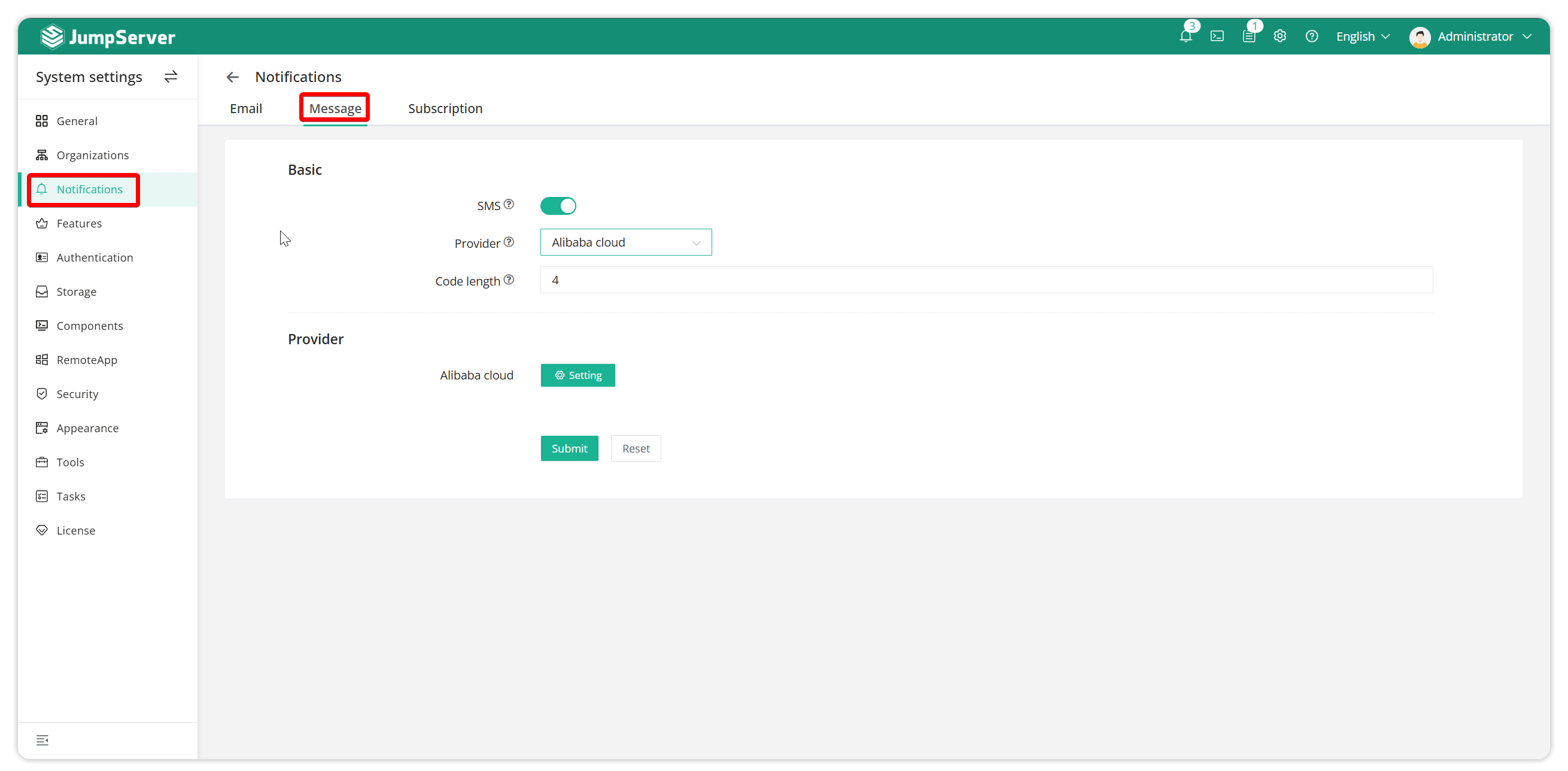
2.4.2 SMS authentication
SMS authentication can be enabled in System Settings - Message Notification - SMS Settings.
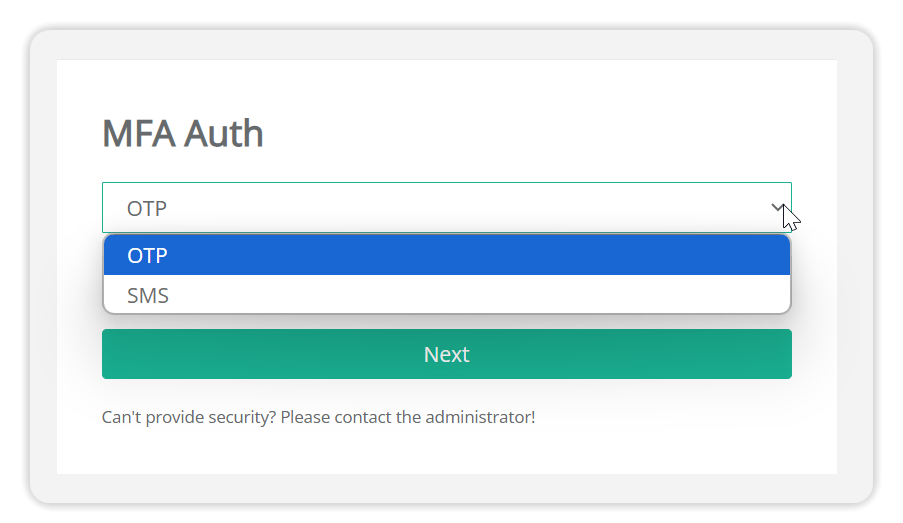
Once set up, you can choose SMS verification where you use MFA.
2.5 User Login Rules
User login restrictions can be refined to the user level. In user management, you can set user login rules for a certain user. You can set rules to restrict users from logging in to specific IP addresses and during specific time periods.
For example, to only allow company IP and working hours to log in to Jumpserver, refer to the following settings.
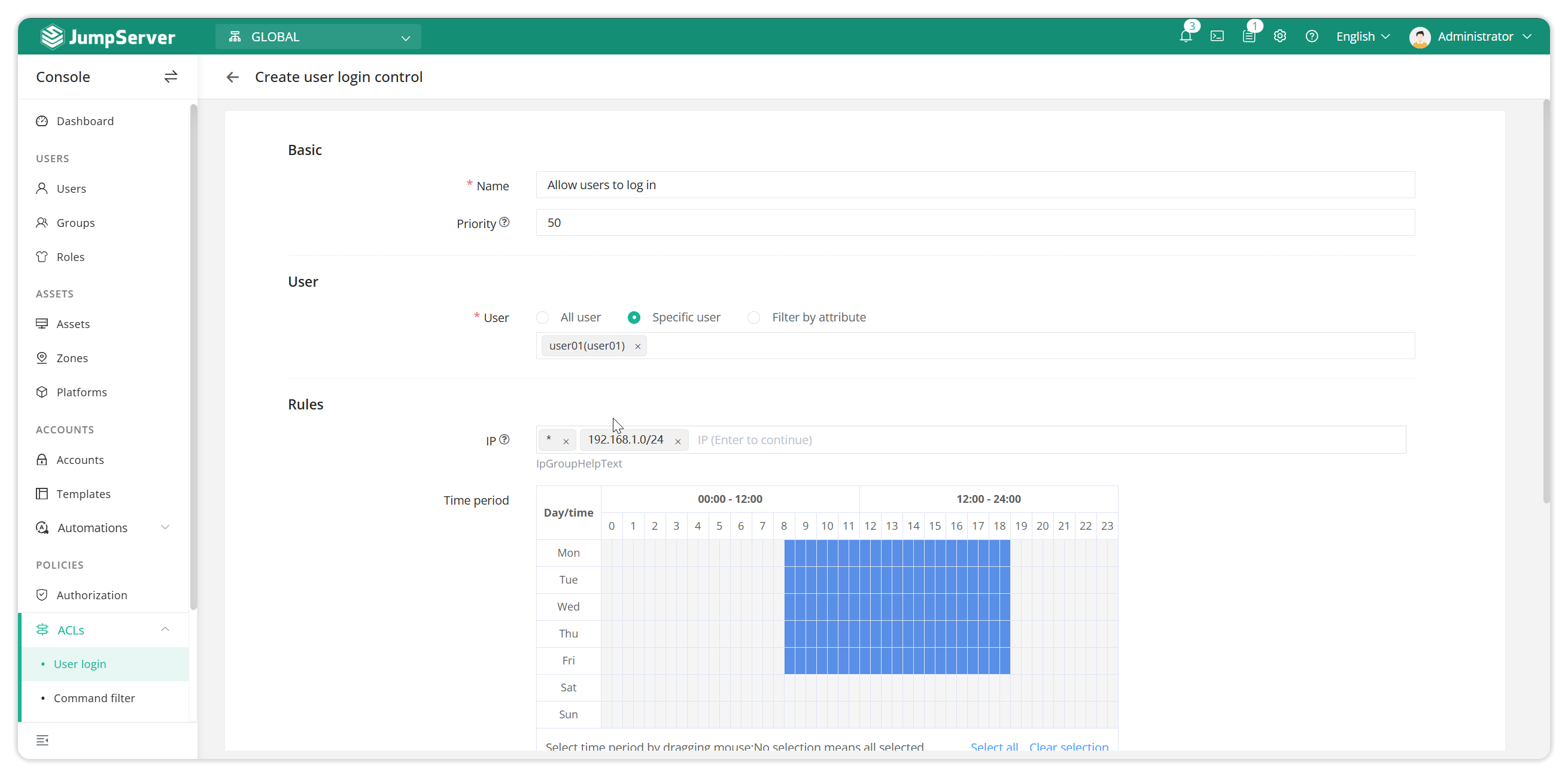
2.5.1 Create rules to allow users to log in
Create a rule to allow users to log in, specify the IP address and time range for login.
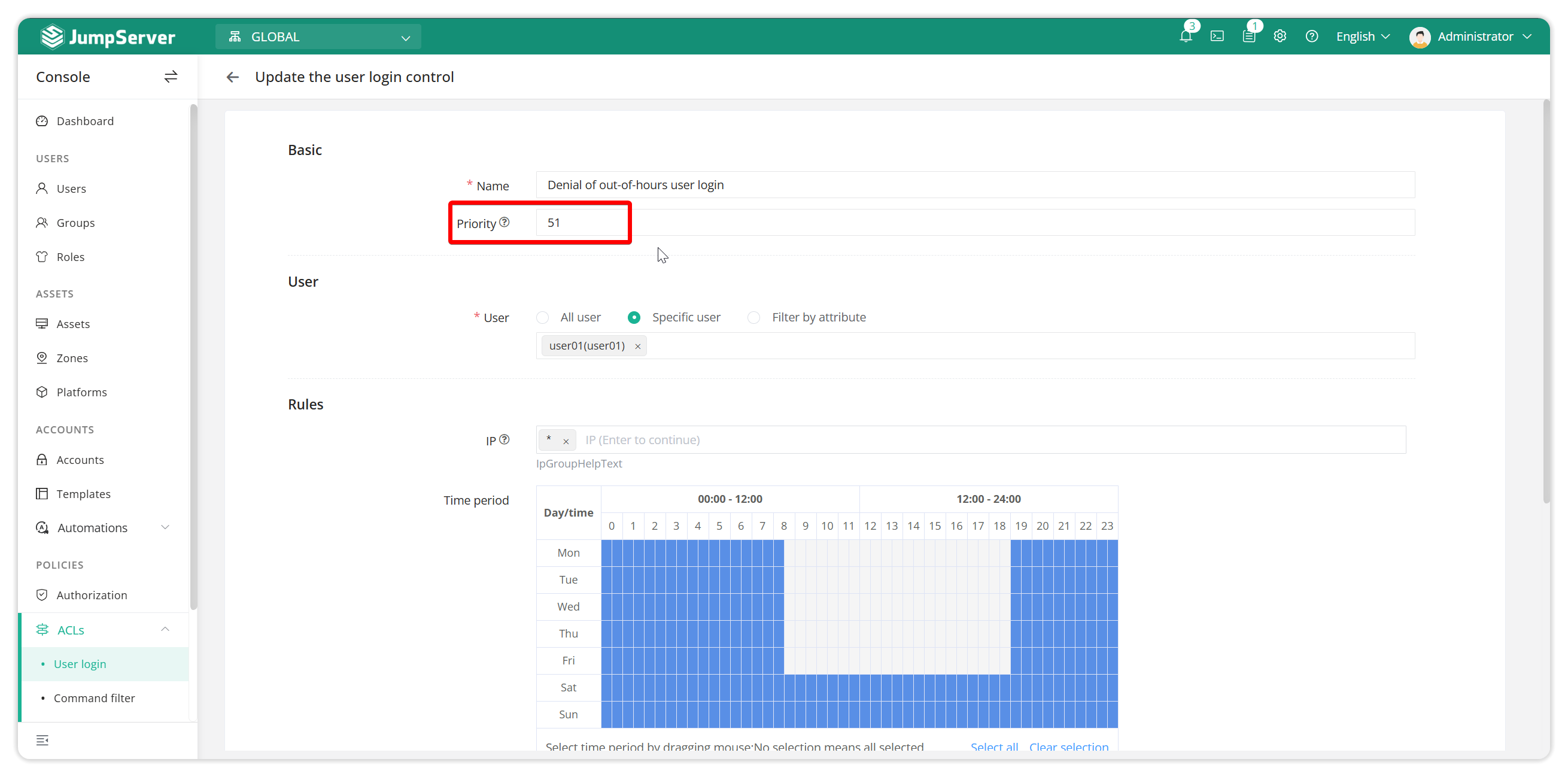
2.5.2 Create a login denial rule
Create a login rule with the action of deny. If the time period is not selected, it means all time. Note that the priority number should be larger than the previous rule.
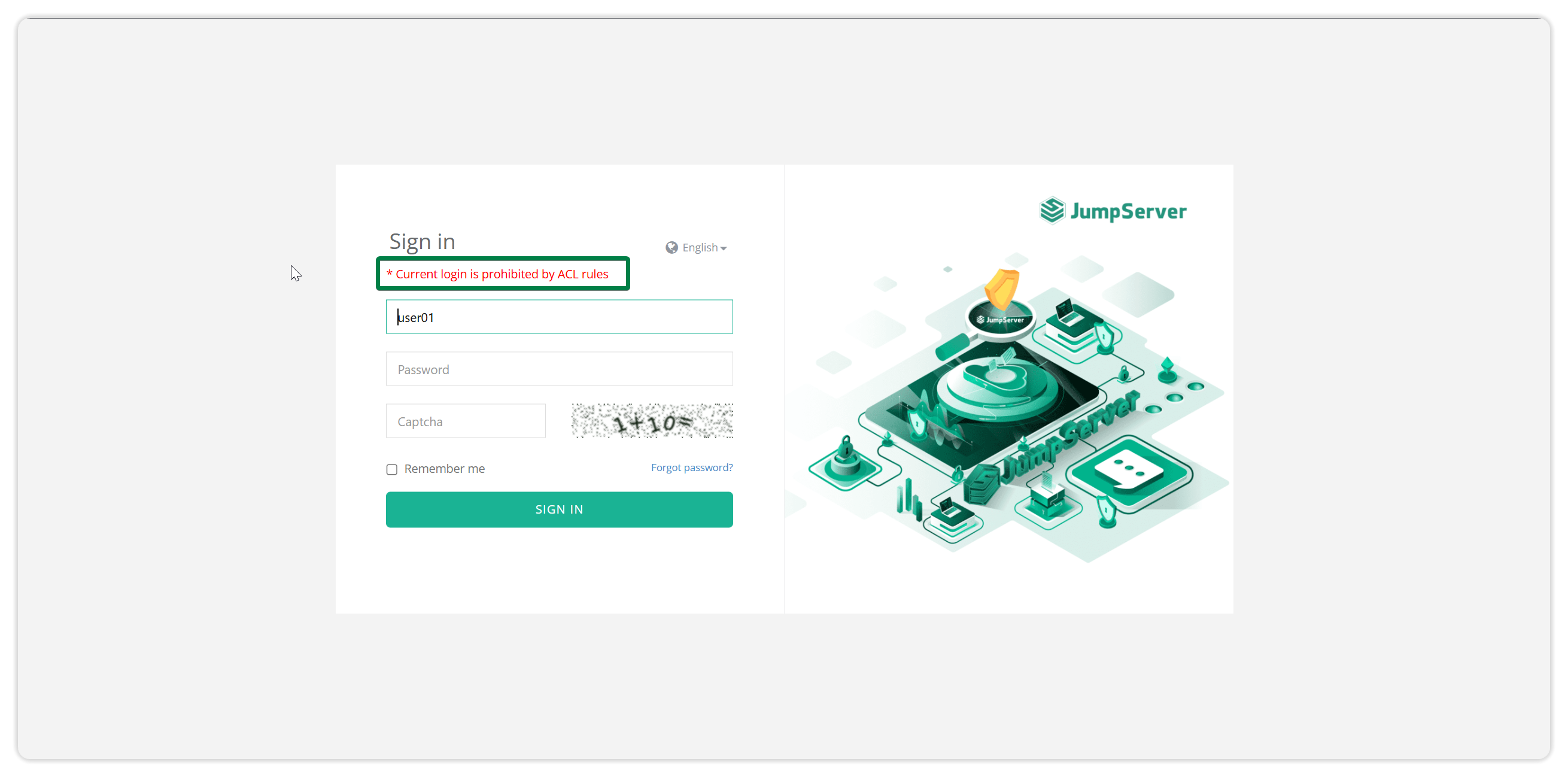
2.5.3 Test login
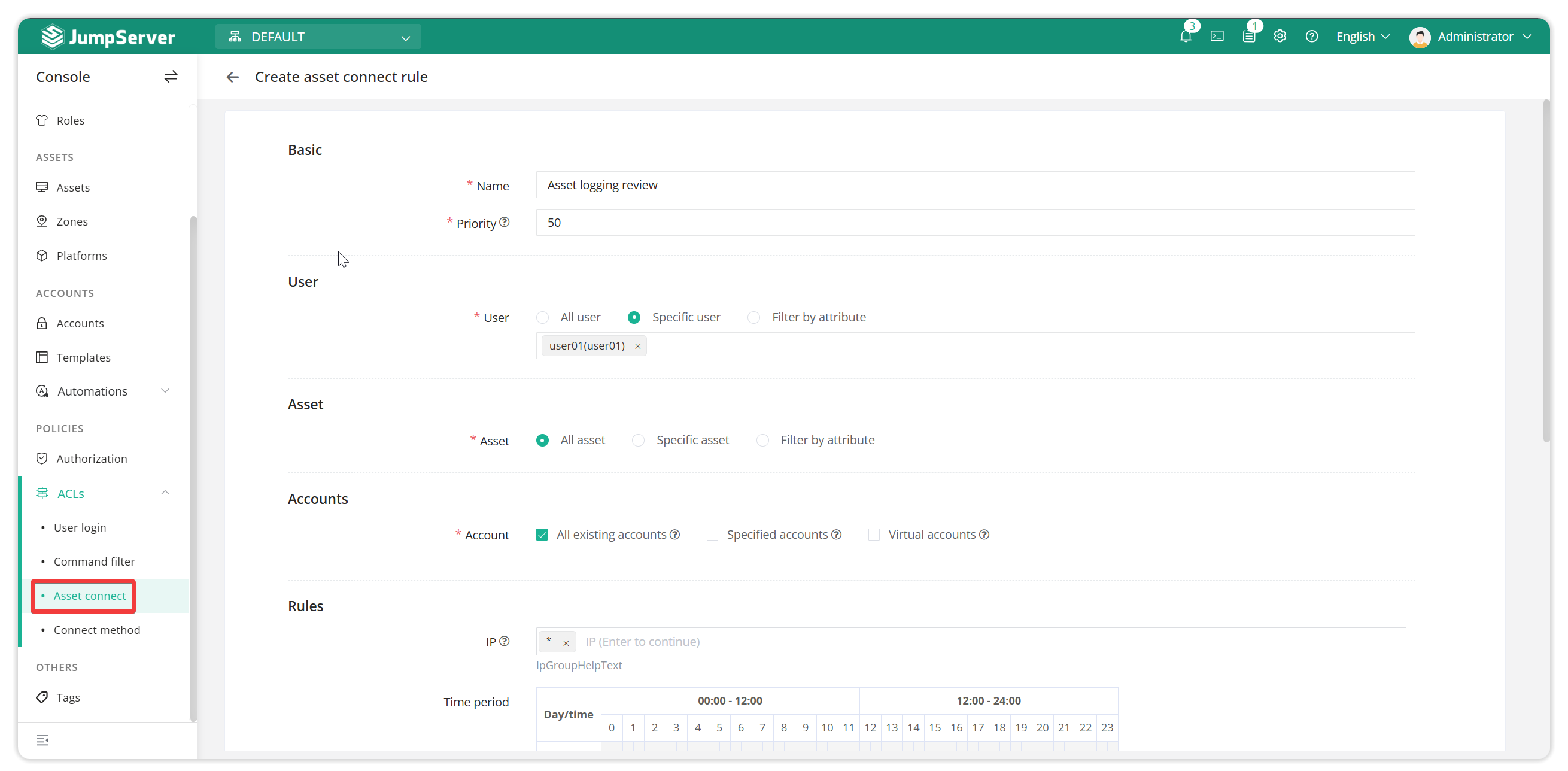
3. Access Rights Control
3.1 Asset Registration Review
This feature is suitable for scenarios where strict access control is required to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive resources. You can also set asset login alarm notifications to identify abnormal user behavior and prevent abuse of access rights.
Based on the security policy, the system can set action restrictions on asset login in four dimensions: JumpServer login user, asset information, account information, and matching rules.
3.2 Apply for asset authorization
Usage scenario: For sensitive assets, users are not permanently authorized, but they need maintenance permissions for the assets at a specific time. Users can actively submit work orders for approval, apply for asset authorization, and specify the asset usage date. After the expiration date, the authorization does not need to be deleted by the administrator, and the authorization rule automatically becomes invalid, reducing the administrator's authorization maintenance costs.
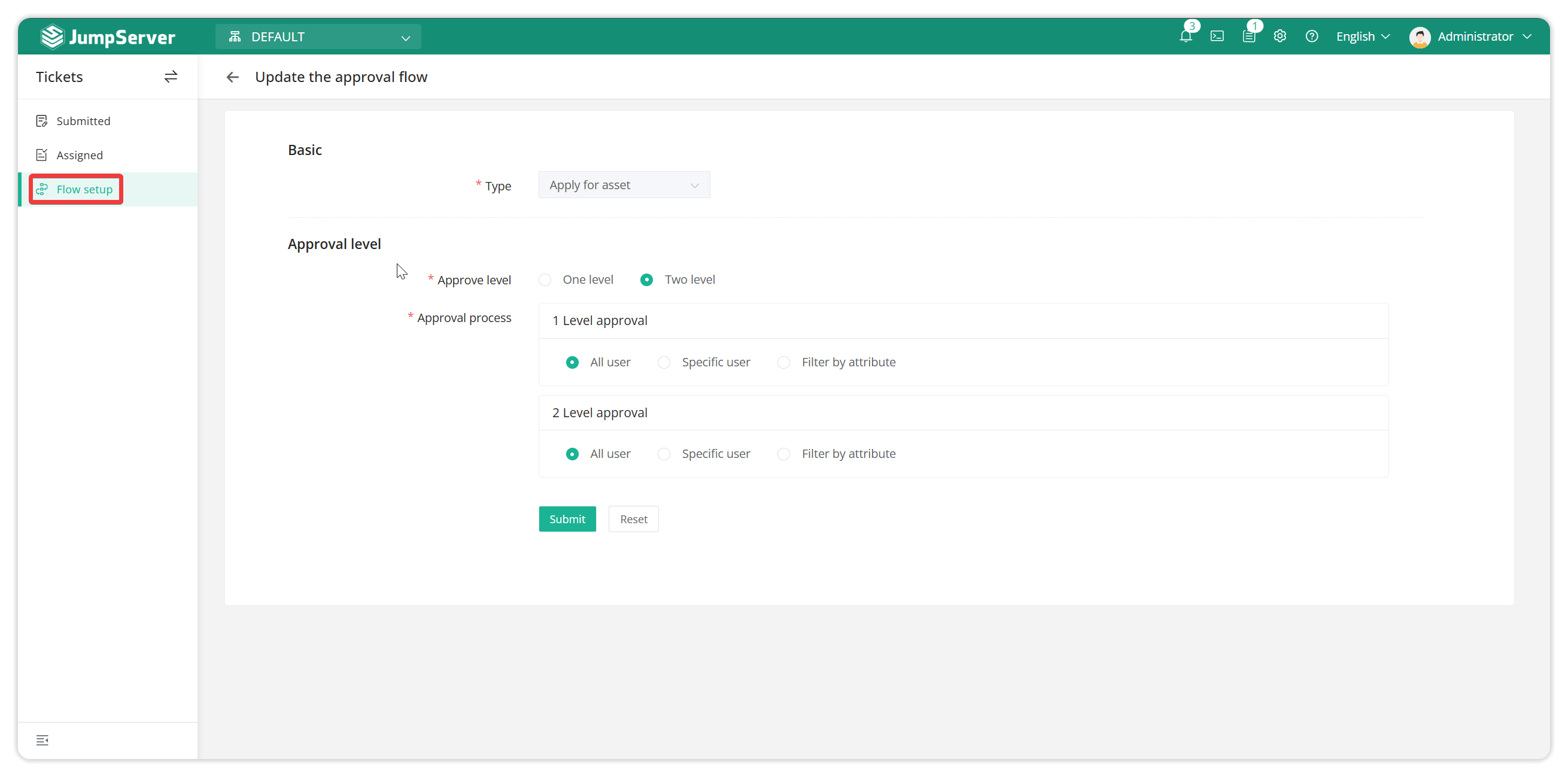
Approval process can specify approvers.