1. Common asset node planning methods
1.1 By business
Business department division: Divide assets according to business departments, such as R&D department, testing department, operation and maintenance department, etc.
Project division: Divide assets by project, with each project corresponding to an asset node.
1.2 By region
Data center division: divided into different data centers, such as Beijing Data Center, Shanghai Data Center, etc.
Geographical location division: division based on the geographical location of the assets, such as domestic assets, foreign assets, etc.
1.3 By environment
Production environment: servers and devices used for formal operations.
Test environment: Servers and devices used for development and testing.
Development environment: The servers and devices used by developers.
1.4 Classification by device type
Server: such as Linux server, Windows server, etc.
Network equipment: such as switches, routers, firewalls, etc.
1.5 Classification by security level
High security level: Servers and devices that store sensitive data, such as core database servers, security application servers, etc.
Medium security level: servers and devices that require a certain level of security protection but do not involve sensitive data, such as ordinary application servers, middleware servers, etc.
Low security level: servers and devices for development and testing purposes, with low security requirements, such as test servers, development servers, etc.
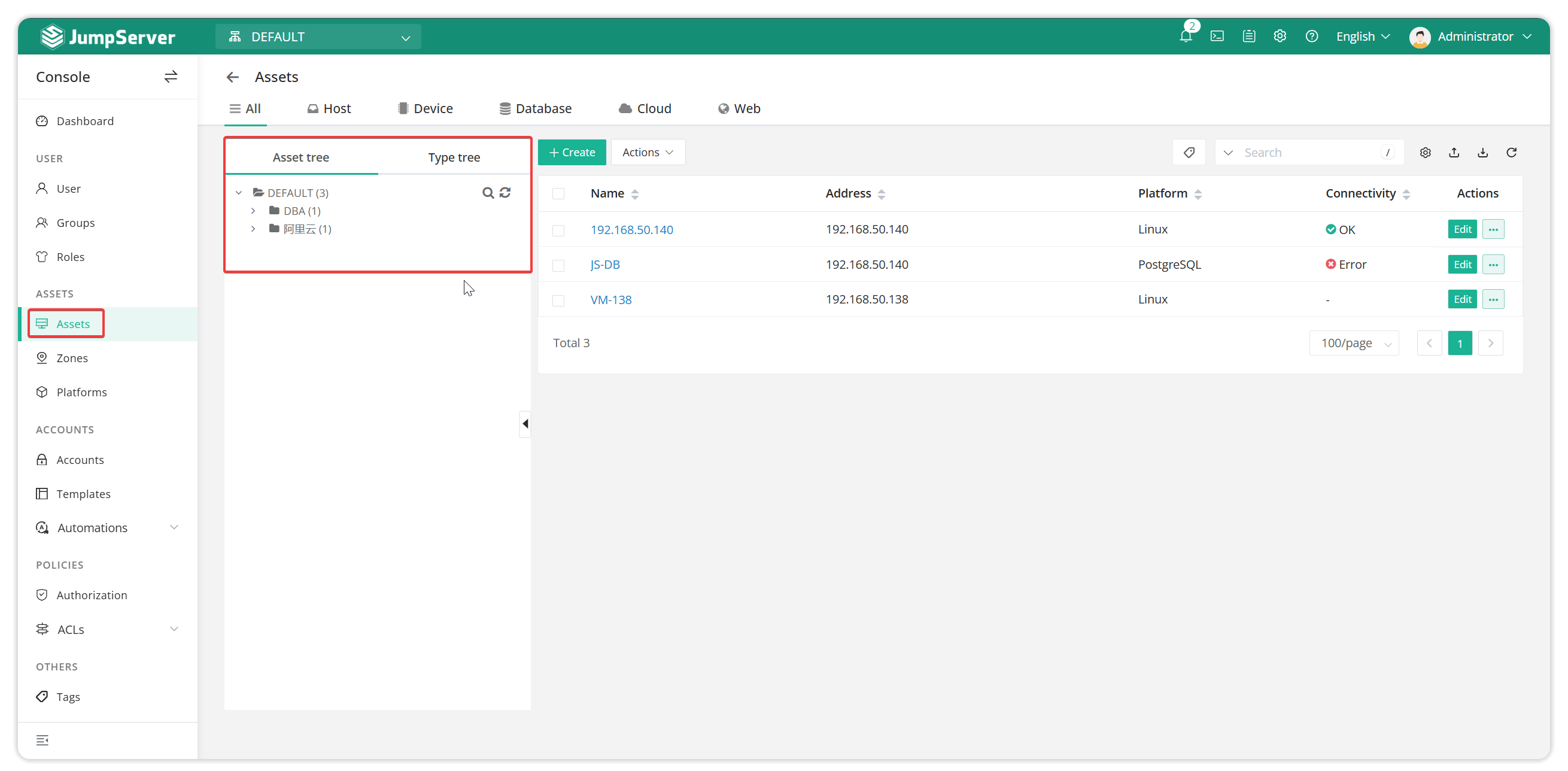
Through the above planning methods, enterprises can flexibly organize and manage assets according to their own needs to improve the efficiency and security of asset management.
2. Usage scenarios of organization management functions
In order to solve the usage scenarios of multiple organizations and multiple tenants in large enterprises, Jumpserver provides organization management functions.Allow one bastion host to be used by multiple parties.
Organizations can be isolated from each other, and administrators can manage users, assets, and authorizations at different levels under the organization, providing users with a more granular management experience.
One bastion host can be used as multiple hosts, which is convenient for management and saves costs.
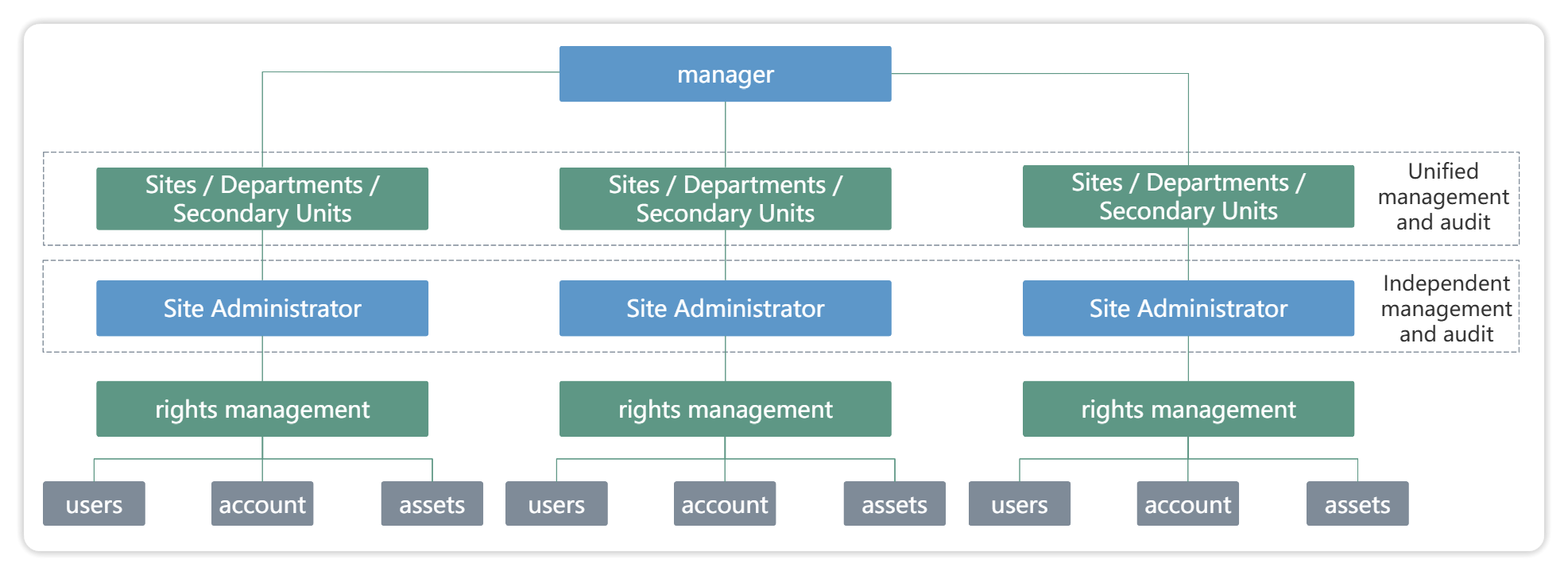
First, plan the entire multi-level management structure, and then combine it with the corresponding unified management standards and operating procedures to delegate relevant authority to each organization layer by layer.
Scene features:
Multi-level management structure with clear authority relationship
Manage layer by layer to achieve decentralization of authority
Unified standards, controllable risk management
3. Configuration of Jumpserver cloud synchronization function
3.1 Overview of Cloud Synchronization Function
Jumpserver can realize automatic management of cloud assets based on public cloud API. Users only need to configure the API access credentials of the cloud account in jumpserver to automatically synchronize all host resource information on the cloud to the jumpserver bastion host.
For users with a large number of cloud assets, the arduous work of importing assets for the first time is saved. In the later operation and maintenance work, when the cloud assets change, jumpserver can also automatically synchronize the latest resource information without frequent manual maintenance.
At the same time, during the cloud asset synchronization process, you can also set synchronization policies to automatically group cloud assets based on their properties.
Currently supported cloud platforms are:Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, Huawei Cloud, Baidu Cloud, JD Cloud, Kingsoft Cloud, AWS (China), AWS (International), Azure (China), Azure (International), Google Cloud, VMware, QingCloud Private Cloud, Huawei Private Cloud, Tianyi Private Cloud, OpenStack, Nutanix, Fusion Compute, LAN, etc.
3.2 Configuration steps
3.2.1 Create a cloud synchronization account
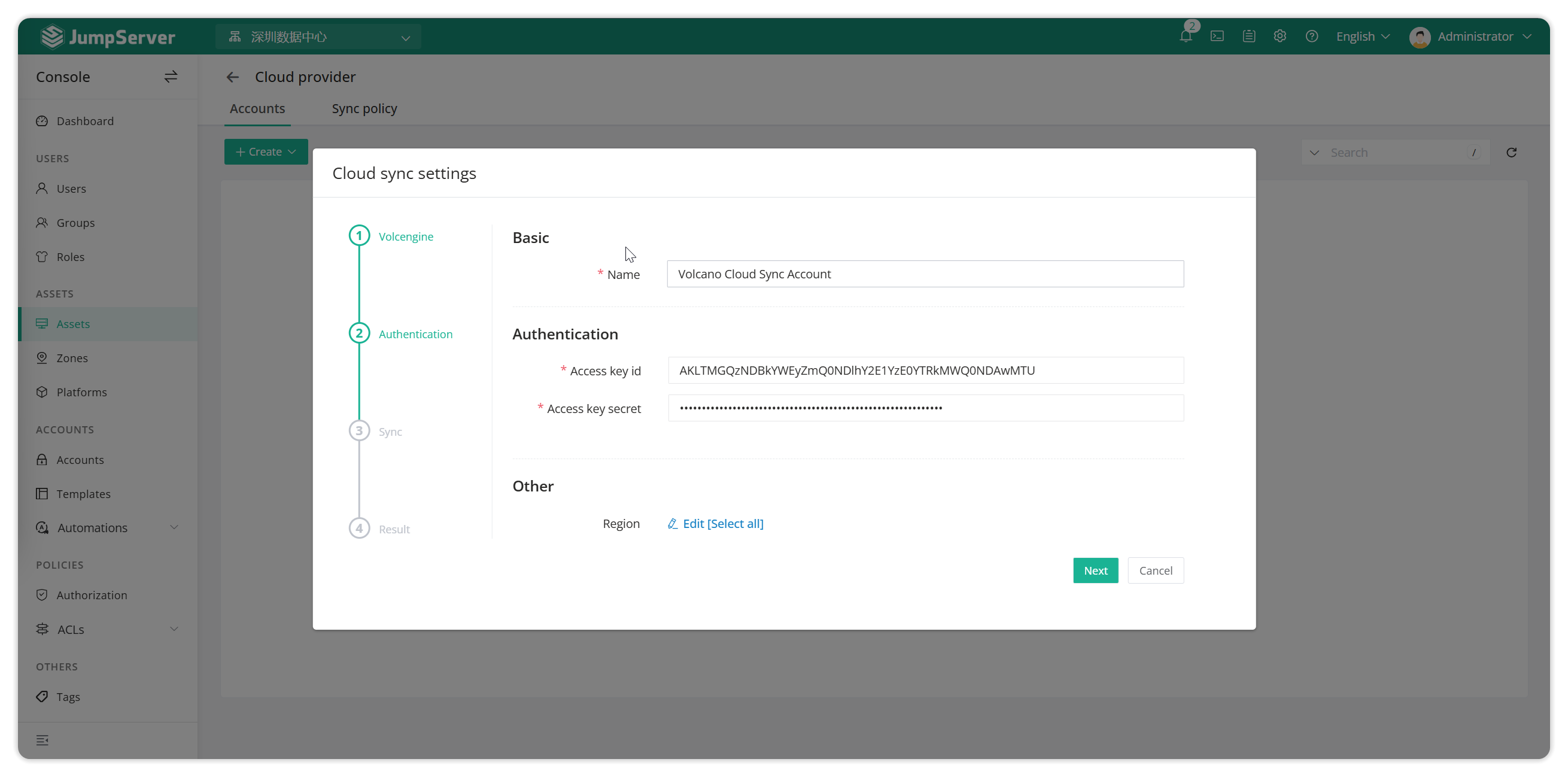
Asset List - Host - Click the Cloud Sync button to enter the Cloud Sync page, click Cloud Account, and create a cloud account on this page.
Take Volcano Cloud as an example (get the relevant key on the Volcano Cloud page).
3.2.2 Create a synchronization strategy
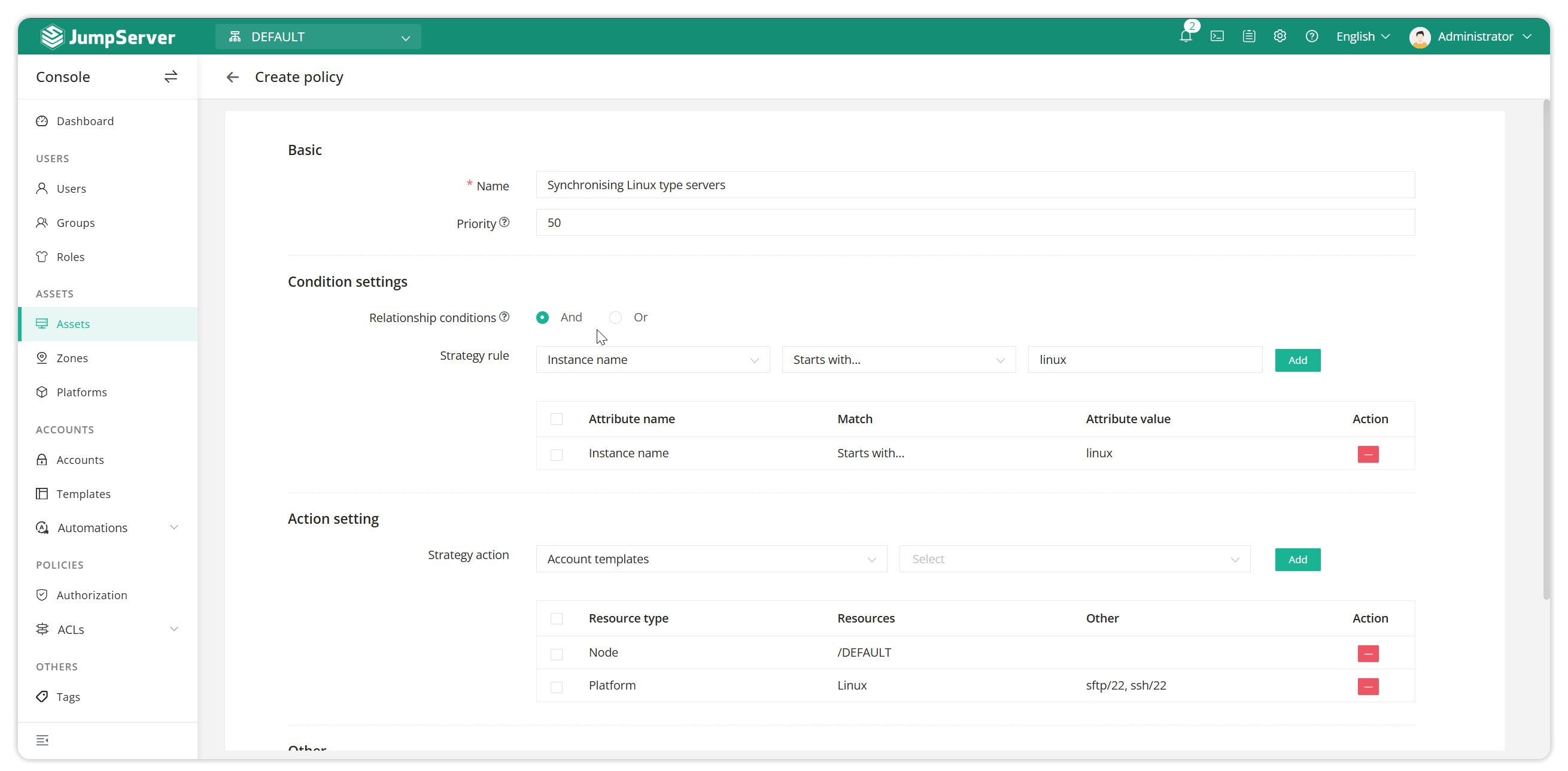
3.2.3 Associative synchronisation strategy
Configure the cloud account and synchronization policy association.
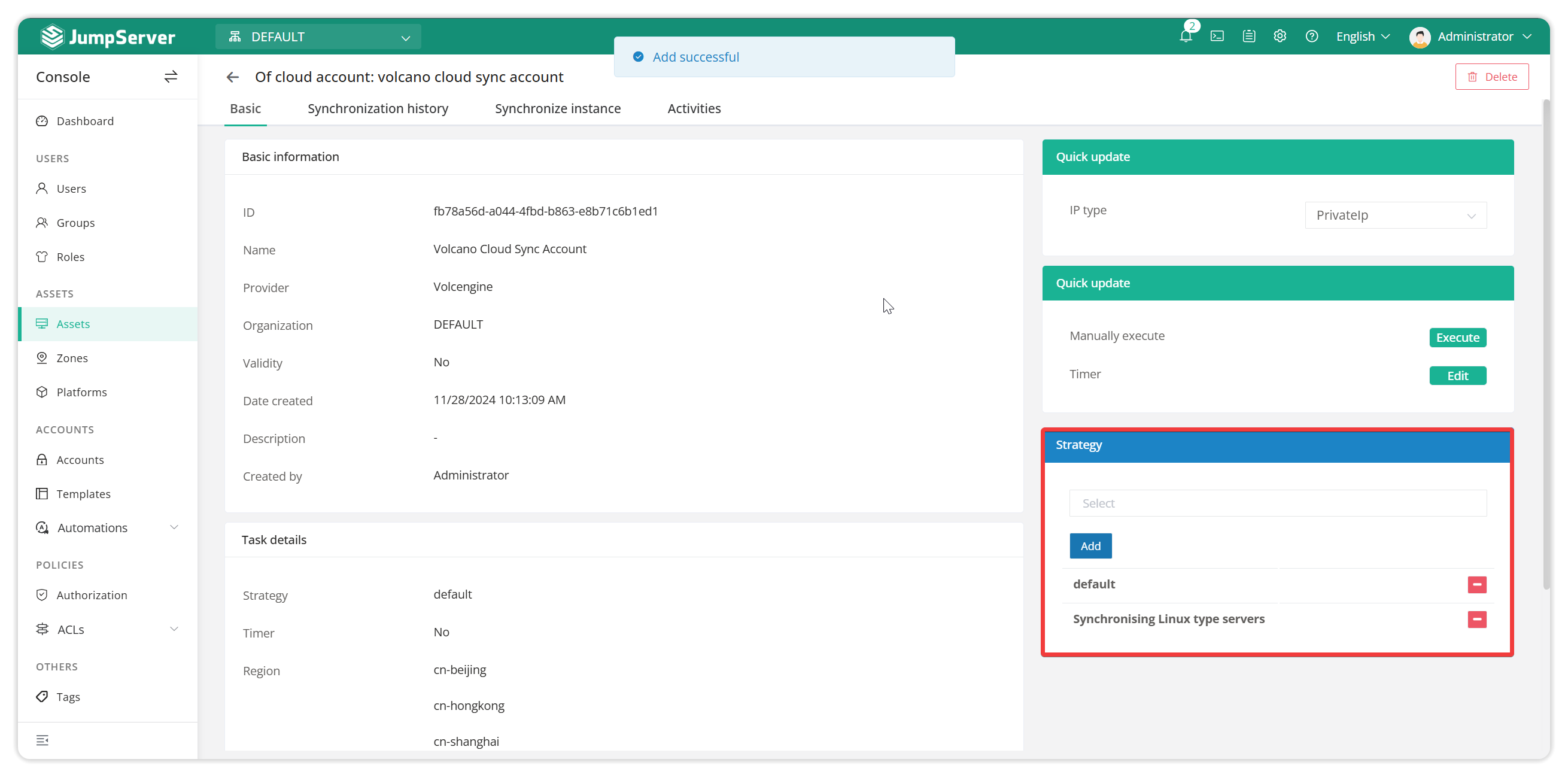
Synchronization tasks can be executed manually or by setting a scheduled task to execute at a scheduled time.
3.2.4 Deleting released assets on the bastion host
Click on the details of the synchronized account - synchronized instance list, more operations - you can automatically delete the released assets.
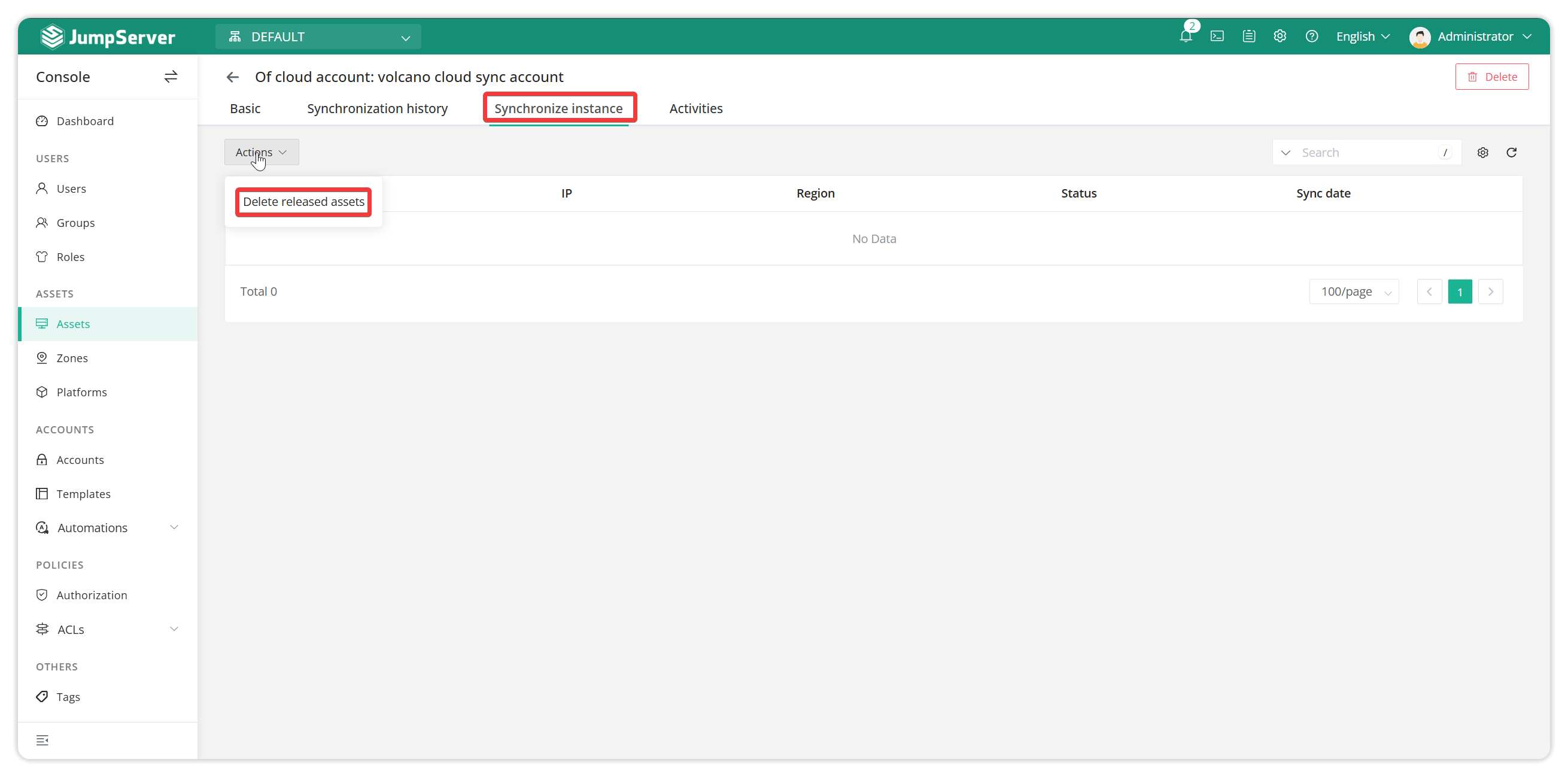
Note: If some assets have been manually added and are also included in the synchronization account using cloud synchronization, you may encounter asset duplication issues and need to manually delete the manually added assets.
4. Jumpserver configuration LDAP authentication
Jumpserver assets use LDAP for login authentication and provide single sign-on functionality through LDAP authentication, which simplifies user management and improves work efficiency.
4.1 Configure ldap authentication information
System Settings-Authentication Settings-LDAP tab.
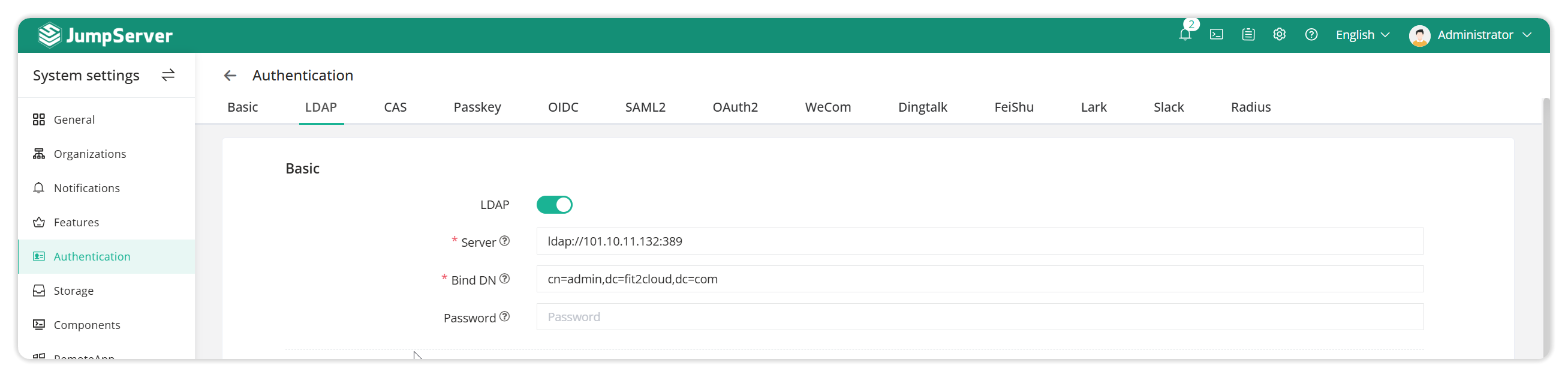
Detailed parameter description:
LDAP address: LDAP address, which can be an IP or domain name. For example: ldap://serverurl:389. Make sure that port 389 of the LDAP server is connected to the JumpServer server.
Bind DN: The LDAP account to bind to. For example: cn=admin,dc=jumpserver,dc=com
Password: The password for binding the LDAP account.
4.2 Configuring User Attribute Mapping
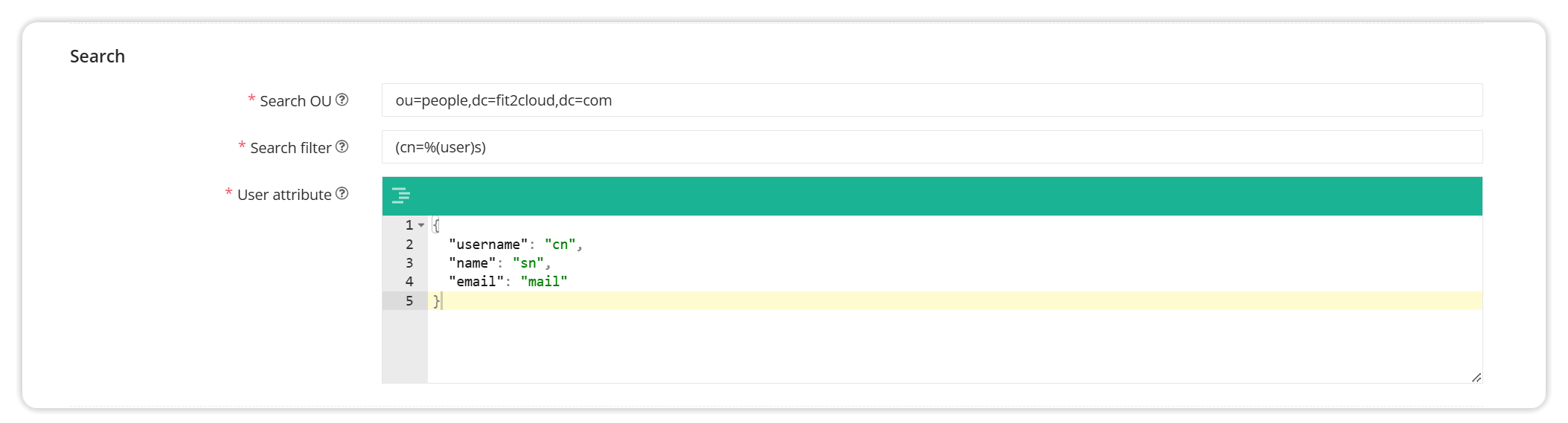
Note: The synchronized user group starts with AD, that is, AD + original user group.
Detailed parameter description:
User OU: The starting OU for user query, filled in according to the LDAP tree structure
User filter: matches the specified user according to the rules. The filter syntax reference is:http://www.ldapexplorer.com/en/manual/109010000-ldap-filter-syntax.ht, generally not modified
User attribute mapping: refers to the correspondence between the attributes in LDAP and the attributes of JumpServer users, and supports the memberOf option. Username, name, and email are the required attributes of JumpServer users.
4.3 Other settings
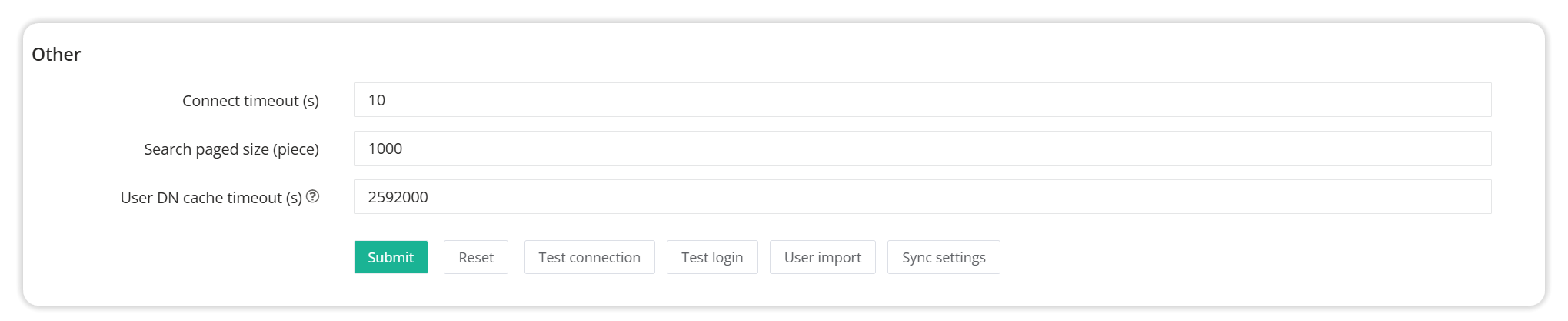
Detailed parameter description:
Connection timeout: The timeout when establishing a connection with the LDAP server.
Number of search pages (entries): The number of pages to be synchronized each time when synchronizing user data from the LDAP server.
User DN cache timeout (seconds): User DN cache timeout
Test connection: This button can detect whether the information configuration is normal and whether the network is connected after the information is configured, and display the number of matching users.
Test Login: This button can be used to test whether the user synchronized with LDAP can log in.
4.4 User Import
After submitting the ldao configuration, click the user import button.
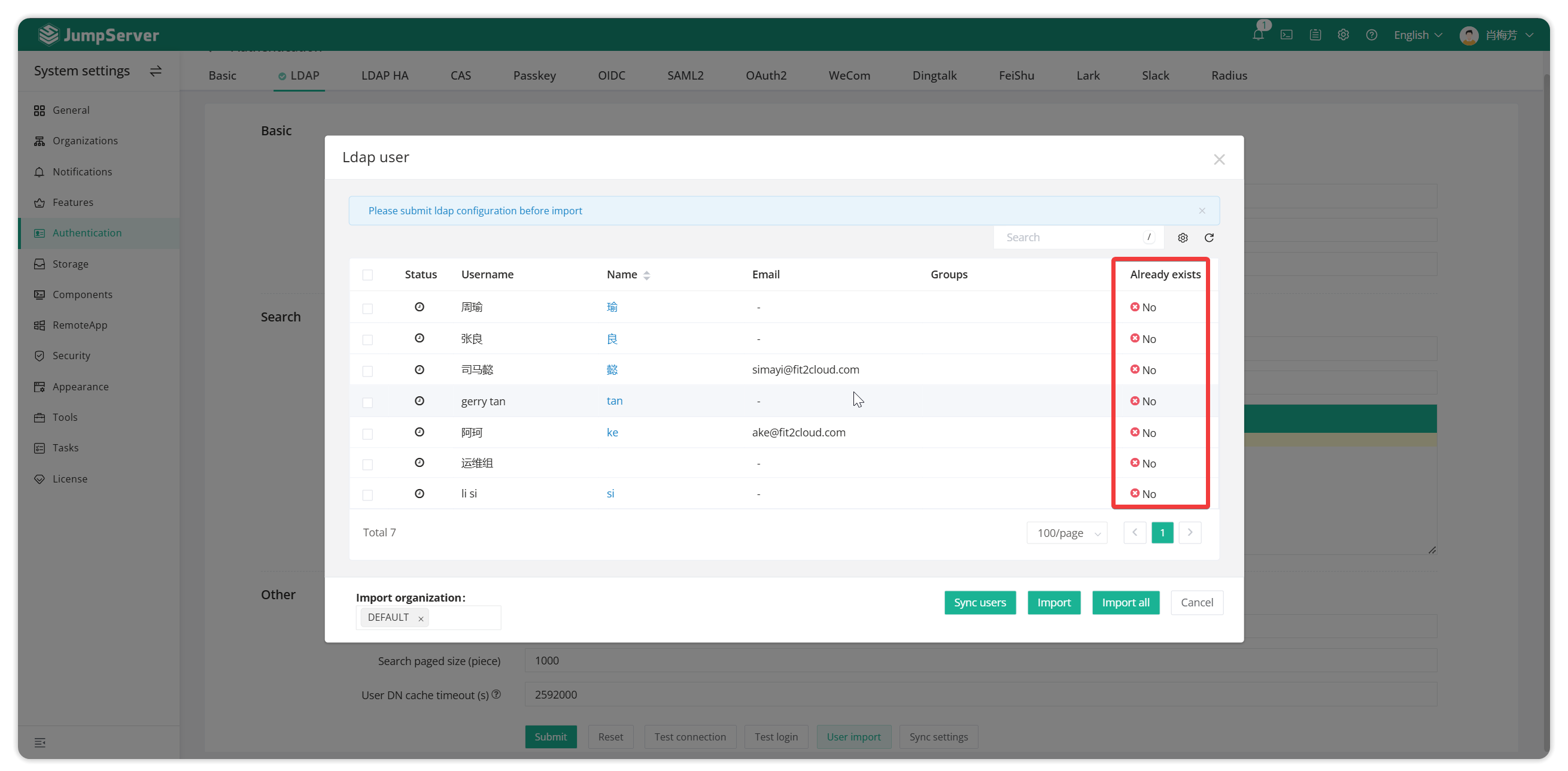
Select the users to be imported or import all.
4.5 Synchronization settings
Can set which organizational structure the imported users belong to, set a scheduled execution, and import users regularly.
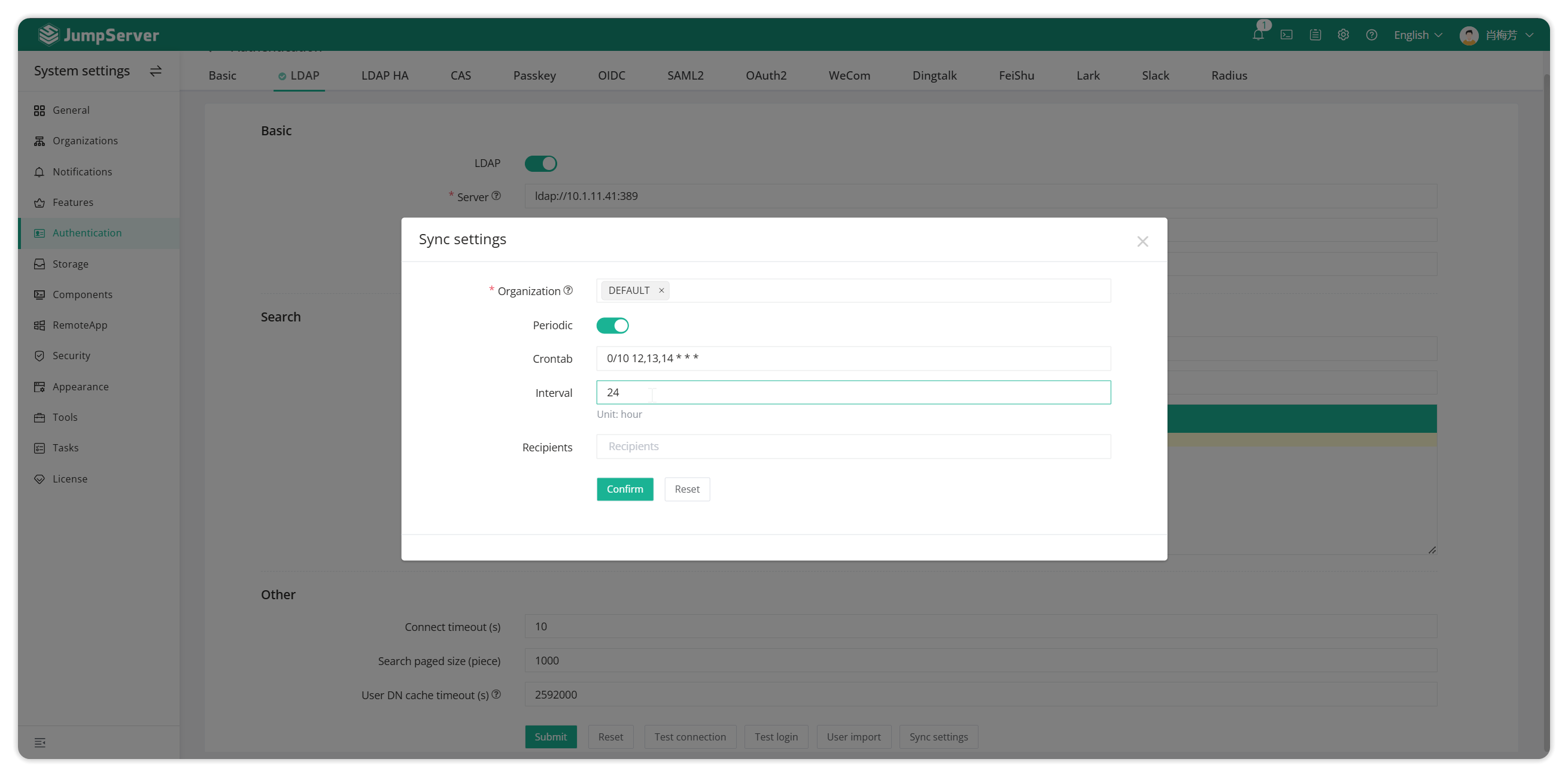
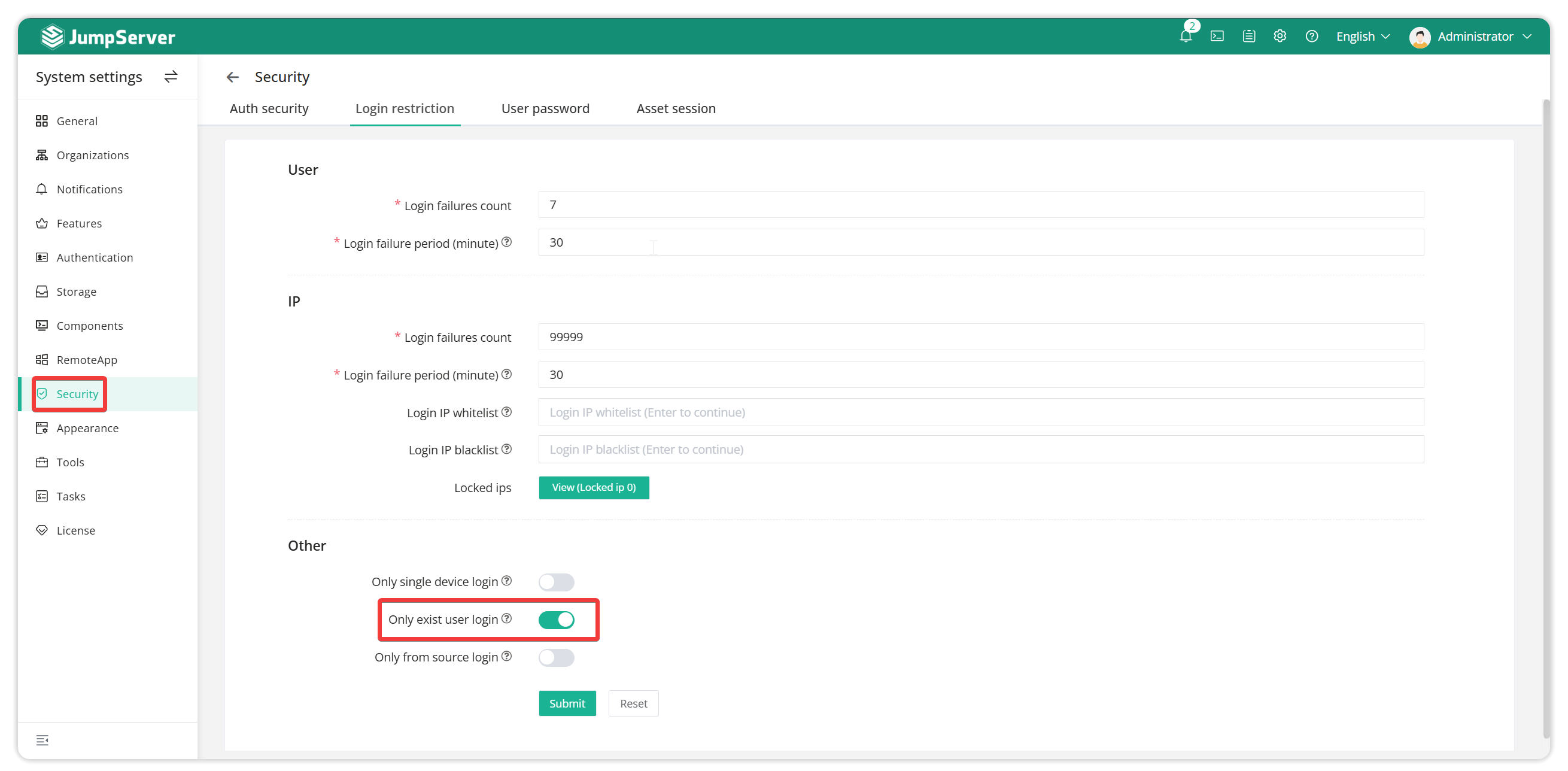
Note:
LDAP accounts that have not been imported into the bastion host will be automatically imported when the user logs in for the first time. To limit the automatic import of the bastion host and only allow the imported accounts to log in to the Jumpserver, refer to the figure below to modify the system settings.