Introduction:
Koko is a component that serves Unix-like operating systems, providing character-based connections via SSH and Telnet and SFTP protocols.
Users can access the target asset by using web terminal integerated in JumpServer or by accessing the target assets using a local terminal like XShell.
Server trace files are stored in the /data/jumpserver/koko/data/logs/ for reference during troubleshooting.
Common Causes:
1. Session Unexpectedly Closed
Cause:
The Cause may be due to sessions not being properly maintained or an administrator setting a disconnect time for asset sessions in the system security settings.
Troubleshooting Tips:
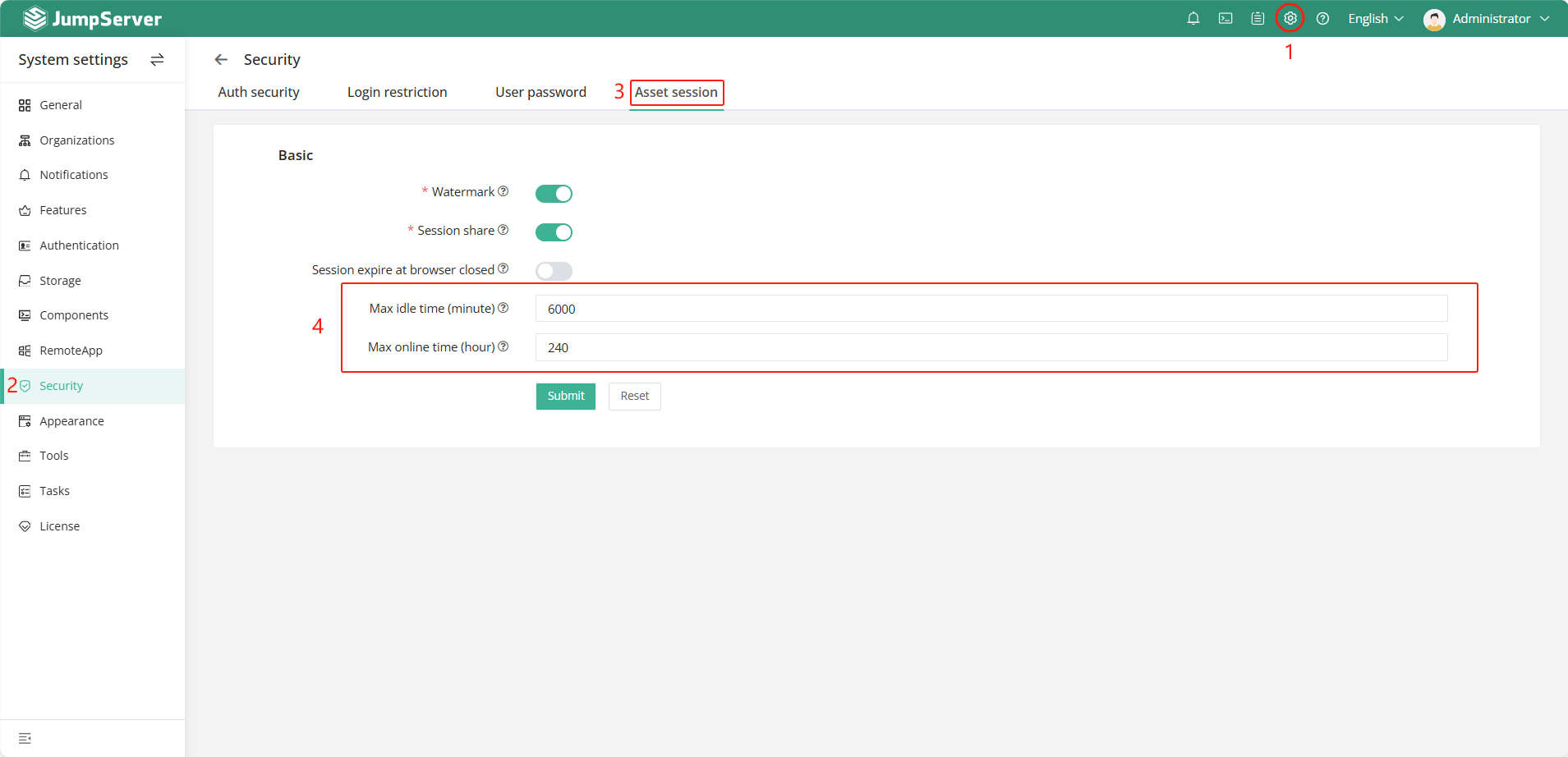
1. Check for multiple layers of reverse proxies. Ensure that the reverse proxy is configured to maintain WebSocket long-lived connections.
2. Check if the asset session in the security settings of JumpServer has a time limit set.

3. Check the stability of the network between JumpServer and the assets.
2. 502 Bad Gateway/504 Timeout
Cause:
The problem may arise due to component abnormalities or incorrect routing configurations for Lion in the Nginx configuration of Koko.
Troubleshooting tips:
1. Check the status of the Koko component. If it is abnormal, you can restart the Koko container by executing the command docker restart jms_koko.
2. Verify the routing configuration for the Lion component in the Nginx configuration of the jms_web component to ensure its correctness.
3. Local Terminal Tools Failed to Access Target Assets
Cause:
This could be due to the user's machine being unable to access the proxy port of the Koko component, typically on port 2222.
Troubleshooting tips:
1. Check if the user's machine can communicate with JumpServer on port 2222.
2. Verify if the Koko component on JumpServer is functioning properly.
4. SFTP Connection Lost
Cause:
This Cause may be due to the SFTP server not functioning properly or restrictions on the Linux account permissions.
Troubleshooting tips:
1. Check the authorization rules to ensure current user has enough permissions to access target path.
2. Confirm that the account has not utilized the "switch user" functionality.
3. Check the available space in the tmp directory to ensure there is sufficient space.
4. Ensure that file uploads from other Linux machines are functioning correctly.
5. Check the configuration file (/etc/ssh/sshd_config) to ensure that the file execution path for the SFTP service matches the actual executable file for SFTP. If they do not match, please modify the configuration to align with the correct executable file for SFTP, and then restart the sshd service.
